Empires of the Word: A Language History of the World (23 page)
Read Empires of the Word: A Language History of the World Online
Authors: Nicholas Ostler
Tags: #History, #Language, #Linguistics, #Nonfiction, #V5


Zi-lu said, ‘If the Prince of Wei were awaiting you, Sir, to take control of his administration, what would be the Master’s priority?’
’The one thing needed is the correction of names!’ the Master replied.
’Are you as wide of the mark as that, Sir?’ said Zi-lu. ‘Why this correcting?’
’How uncultivated you are, Yu!’ responded the Master. ‘A wise man, in regard to what he does not understand, maintains an attitude of reserve. If names are not correct then statements do not accord with facts. And when statements and facts do not accord, then business cannot be properly executed. When business is not properly executed, order and harmony do not flourish. When order and harmony do not flourish, then justice becomes arbitrary. And when justice becomes arbitrary, people do not know how to move hand or foot. Hence whatever a wise man states he can always define, and what he so defines he can always carry into practice; for the wise man will on no account have anything remiss in his definitions.’
Confucius,
Lúnyŭ
†
(Analects), xiii:3 (Chinese, early fifth century BC)
2
Two ancient languages, widely distant in their lands and their eras, are yet strangely similar in their careers. In their attributes they are unmatched, except by each other.
Egyptian and Chinese are both vehicles of single cultural traditions of immense prestige. For each, the role as universal language was uncontested in their homeland. By the dawn of their recorded histories they were already established over the central zone of the lands where they were to be spoken. Each maintained this position of solitary and basically unchanging dominance for an awesome period of over three thousand years, or more than 120 generations. Yet, in each case, despite the fame and prestige of the culture among neighbours, who were often dominated politically by these powers, the languages never assumed any role as lingua franca beyond the territory that they considered their homeland.
Another parallel concerns their scripts. Each language originated its own unique system of writing, based on pictograms in a particular style; and each of these scripts early attained a form that would not change. Each was later taken up by another people, and simplified to yield the basis for a phonetic writing system: Egyptian hieroglyphs were the starting point for the Phoenicians’ alphabet, and the Japanese drew their
kana
syllabary from Chinese characters. But in each case the original language culture disregarded the innovation, and maintained its ancient system essentially unchanged, despite the vast overhead this entailed in continuing lengthy scribal education.
Their careers are parallel. For us, their main interest lies in considering how a language can achieve steady state, a kind of homoeostasis where it appears to absorb any perturbation that might affect it. This steadiness is particularly interesting in the cases of Egypt and China, since the languages have not simply survived in isolation, but can be seen coping with human incursions for much of their history, and occupy spaces large enough to pose difficulties for a unitary government.
Another aspect of this puzzling unity, especially in the case of Chinese, is the strange coherence of the language itself. Certainly Chinese has dialects, and they are different enough often to be considered distinct languages. But this famous fact is less interesting than a less noted one: over 70 per cent of Chinese speakers speak a single variety, known as Mandarin or Pŭtōnghuà,
*
and this, the official language of the Chinese state, is spoken in more than 75 per cent of the country’s area. It has some local accents but essentially no internal variation. Since both the Chinese population and surface area are vast, the degree of uniformity so achieved is unparalleled in any other known language. We need to consider how it could have come about.
The two also have some direct implications for the modern world.
Egyptian, after all, did ultimately succumb to the incursions of its neighbours, carried out with steadily increasing permanence by waves of Assyrians, Persians, Greeks, Romans and Arabs, and now survives, if at all, as Coptic, in the liturgy of what was a foreign religion, Christianity. There is evidence here of what it takes to obliterate a seemingly eternal tradition in the land of its birth. How is immortality undone?
By contrast, Chinese, for all the political reverses and atrocities its people have suffered at the hands of heartless foreigners in the last two centuries, has never been stronger than it is today. Its speakers make up one sixth of the world’s population, and it has three native speakers for every one of English. Nevertheless, over 99 per cent of them live in China, so it cannot be considered a world language—unless China is your world. Those who speak it often call it
zhōng guô huà
, ‘centre realm speech’: in that at least Chinese ethnocentrism is undiminished. There is still time to consider those forces that have kept the Chinese realm so firmly, and compactly, centred on its traditional homeland: will they still prevail in the modern world?
The remarkable similarity of the careers of the Egyptian and Chinese languages can first be displayed in the form of two chronological charts. Foreign incursions and cultural influences are marked in boldface type.
Both Egyptian and Chinese history are made up of long periods of stable unitary government, interspersed with intervals of civil unrest, or at least disunity, when there were competing dynasties in different parts of the countries. Egypt has three such periods of stable self-government, the Archaic + Old, the Middle and the New Kingdoms, followed by a Late Period, when foreign rule was the norm rather than the exception. China also has three long periods of indigenous rule, the feudal age of the Shang and Zhou dynasties, the First Empire of the Qin and Han dynasties, and the Second Empire of the Sui, Tang and Song, which then were overlaid by a succession of partial or total alien invasions.
Both civilisations were formed originally along the valley of a single river, the Nile
*
and the Huang-he (’Yellow River’) respectively, although China expanded to take in the next great river valley to the south, the Yangtze Kiang.
†
And both civilisations demonstrated that, although they were not capable of defending their borders indefinitely, successful invaders stood to be absorbed in the long term. The linguistic analogue of this was that no foreign invaders imposed their language on the population, nor indeed (until the Persians and then the Greeks took Egypt) managed to retain their own language for more than a generation after mastering the country.
These are both tales of solid growth and heroic maintenance, rather than massive spread. This chapter first sketches each language’s history, particularly noting the encounters with languages spoken by foreign intruders: these often came to stay, but tended not to supplant their hosts. Armed with the facts, we can then consider what might be the secrets of such language stability.
Be a craftsman in speech, thou mayest be strong, the tongue is a sword to a man, and speech is more valorous than any fighting …
Instruction for King Medicare, line 32 (Egyptian, mid-twentieth century BC)
3
The origin of the Egyptian language must be found close at hand, in the Afro-Asiatic or Hamito-Semitic family whose descendant languages cover most of North Africa and the neighbouring areas of the Fertile Crescent (from Palestine round to Iraq) and Arabia. Egyptian has no close relatives in this large family, but its family origins do account for some of its characteristic features, mundane things such as the fact that feminine nouns end in -t.
§
Archaeology shows that the Egyptian state was established first in the late fourth millennium BC, in the region surrounding the great salient of the Nile which was later dominated by the city of
Wast
(known to the Greeks as Thebes), hence in southern or ‘Upper’ Egypt. It is apparent that Egyptian was already the language spoken, since there are legible hieroglyphic captions on labels and pots in the royal cemetery in this area, at Abydos, from the early third millennium. In fact pre-dynastic sites, of this so-called Nagada culture, have been discovered along the whole length of the Nile from Aswan to the delta and including the Faiyum, showing that the whole area of ancient Egypt was already occupied. Since the surrounding desert remained uninhabitable, the kingdom of Egypt was always a ribbon development along the Nile. Traditionally, its history begins when King Menes unified the Upper and Lower lands, and set up his capital at
Min Nafər
(Memphis) in Lower Egypt.
This achievement remained a matter of legend rather than history, since the king’s name cannot be identified with any of the hieroglyphic evidence, and there is no written evidence of separate kings in the north and south. Nevertheless, there was a tradition of differently shaped and coloured crowns for the two kingdoms, unified formally in the historical crown of the pharaoh
†
(in a way reminiscent of the composite character of the Union Jack). And the name by which the Egyptians always knew their own country was
TaRwəj
, ‘the pair of lands’.
Thereafter, Egyptian has no history, in that it had achieved its historic domain, the Nile valley from the first cataract to the sea. Although Egyptian power would expand periodically and withdraw again, up the Nile into Kush and north-eastward over Palestine and Syria, the language did not spread with it. For almost four thousand years its range stayed the same.
Nevertheless, spoken Egyptian did change phonetically and syntactically over this time. The classical language of Egyptian literature was refined and established in the third millennium. Known as ‘Middle Egyptian’, its use was maintained in writing as far as possible until the end of Egypt’s civilisation, above all in formal and ritual texts. But evidently the language gradually changed on the lips of its speakers. Among a host of finer periods, linguists distinguish broadly an earlier era (3000-1300 BC) from a later one (1300 BC-AD 1500). From the middle of the second millennium, it is clear that the spoken language had moved on significantly.
On the simplest level, the sounds of the language change: r and the feminine ending
t
are lost at the end of words, and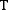 (ch in
(ch in
church
) and
d
(j in
judge
) are simplified away, replaced by simple
t
and
d.
But there are structural changes too. They are reminiscent of the way in which Italian came to differ from Latin, or Middle English from Anglo-Saxon. In the older period, Egyptian had been highly inflected, with a set of endings for number and gender; it had had no definite or indefinite article (corresponding to English
the
or
a
); and the characteristic word order had the verb first in the sentence, followed by subject and then object. In the later period the noun endings tend to be lost, but articles come into play, expressing the distinctions in a different way. The verb system becomes more dependent on auxiliaries, and so less highly inflected. Furthermore, the subject now tends to come first in the sentence (as it does in modern English).
