Headache Help (16 page)
Authors: Lawrence Robbins

SIDE EFFECTS
: Fatigue and weight gain, although no side effects may occur. Nausea, stomach upset, and sedation sometimes also occur. With higher doses, hair loss or a tremor in the hand may occur. These tend to be related to the dose and may subside if the dose is lowered. Do not use Depakote if you might be pregnant.
2. A
NTIDEPRESSANTS
Although these medications are commonly used at high doses to combat depression, that’s not why they are recommended here. Some of these drugs, such as amitriptyline and other similar so-called tricyclic antidepressants, are useful because they tend to increase the concentration of serotonin in the brain. Newer antidepressants, which are not tricyclics, like Prozac, Zoloft, and Paxil, also influence serotonin.
Prozac, Zoloft, Paxil, and the other newer antidepressants are somewhat less effective for pain than the older ones, such as amitriptyline. However, these newer medications have considerably fewer side effects and are more effective for anxiety and depression in low doses than the older drugs. They are all helpful for chronic daily headache as well. All of these antidepressants are useful for panic disorder. In addition, they are used in people with bipolar illness (manic-depression), usually in conjunction with a “mood stabilizer,” such as Depakote or lithium.
Prozac, Zoloft, and Paxil have been widely used for at least ten years now, and the fears for long-term side effects are diminishing. While no long-term side effects have been identified, it may take decades before we can definitely say that they are completely safe for the long term. However, tens of millions of people have been on these medications for long periods of time.
Note: Many of these medications can influence heart rate, increasing the risk of a rapid heartbeat. For that reason, they are prescribed with caution for the elderly and are sometimes used with a beta-blocker (the next group of drugs we’ll discuss) to lower the pulse rate.
- A
MITRIPTYLINE
(E
LAVIL
)
This is the most commonly prescribed antidepressant because it is effective, inexpensive, and can help you sleep. It is particularly useful if you get both daily tension headaches and migraines.
TYPICAL DOSE
: It is important to begin with only 10 mg, which may be all many people can tolerate, taken at night, working up to 25 or 50 mg (doses far below those used to treat depression) in several weeks. The dose can be pushed up to 150 or 200 mg if needed. Some people do well with as little as 5 mg (half a tablet).
SIDE EFFECTS
: Sedation (which decreases over time), weight gain, a dry mouth (which can be countered with Oral Balance Gel or Biotene toothpaste), constipation, dizziness. Occasional anxiety or nervousness, which will usually decrease in time. Less common side effects are depression, blurred vision, memory difficulties, and insomnia (although usually amitriptyline induces sleepiness). - F
LUOXETINE
(P
ROZAC
)
A very well-tolerated antidepressant that is less effective for pain but has far fewer side effects than amitriptyline and the other older antidepressants.
TYPICAL DOSE
: Doctors begin with a low dose of these medications and watch for any anxiety or nervousness that may occur. After several days or a week, however, these reactions usually stop. These medications are excellent in treating anxiety and nervousness, but in the beginning they may actually exacerbate them. With Prozac, doctors usually begin with half a 10-mg tablet in the morning, and then, if necessary, increase the dose to 20 mg or higher over days to weeks. The key is to begin with low doses. Prozac is available in 10-mg, 20-mg, and 40-mg capsules and 10-mg tablets; liquid Prozac is also available.
SIDE EFFECTS
: Initial anxiety or nervousness is relatively common. Insomnia, a feeling of spaciness, and fatigue may occur Occasionally, people experience sweating, weight loss or weight gain, or tremors. If you are extremely agitated or up all night with these medications, it is best to stop them and call your physician.
Sexual side effects (decreased ability or decreased sex drive) are relatively common with many antidepressants. Prozac, Zoloft, and Paxil cause these sexual side effects in many people. In fact, they are one of the main reasons why people discontinue taking them. Minimizing the dose is crucial for minimizing the side effects. The antidepressant Wellbutrin (see section below on Miscellaneous Antidepressants) tends to cause fewer sexual side effects. - S
ERTRALINE
(Z
OLOFT
)
Similar to Prozac, Zoloft is extremely well tolerated and very useful for anxiety, depression, and chronic daily headaches. However, these newer antidepressants are less effective for pain and headaches than amitriptyline and the other older (tricyclic) antidepressants. Some people tolerate Prozac but do poorly on Zoloft, and vice versa. You may want to try several of these antidepressants, therefore, before you give up on them.
TYPICAL DOSE
: One or half a 2 5-mg tablet to start, increasing over four to six days to 50 mg. The usual dose for headaches is low, 25 mg to 75 mg per day. For depression, 75 mg to 150 mg (or more) is often prescribed. Zoloft is available in conveniently scored tablets of 25-mg, 50-mg, and 100-mg doses, and may be taken once per day. With most of these medications, all of the doses are the same price, so using a higher strength tablet and cutting it in half is usually less expensive.
SIDE EFFECTS
: Similar to Prozac—generally milder than the older (tricyclic) antidepressants. - P
AROXETINE
(P
AXIL
)
Very similar to Prozac and Zoloft, Paxil is also available in very convenient scored tablets of 10-mg, 20-mg, 30-mg, and 40-mg doses. Paxil is very well tolerated, but if you are on more than 10 mg per day and suddenly stop the medication, you may experience mild withdrawal symptoms for two or three days. These symptoms are flulike feelings, with tiredness.
As with the others antidepressants, Paxil is very useful in some patients for chronic daily headache, and of course, for anxiety or depression.
TYPICAL DOSE
: One or half a 10-mg tablet, for four to six days, increasing slowly to 20 mg per day. The usual dose for headaches is low, 10 mg to 30 mg per day. The usual depression dose is 30 mg or 40 mg (or more) daily. It is crucial to begin with low doses.
SIDE EFFECTS
: Similar to Prozac. - D
OXEPIN
(S
INEQUAN
)
Very similar to amitriptyline, doxepin is extremely helpful for migraines and tension headaches, as well as anxiety.
TYPICAL DOSE
: Usually begins with only 10 mg, to be taken at night, which is all that many people can tolerate; if tolerated, the dose may be slowly increased to 50 or 75 mg and up to 150 mg or more, but if 150 mg is not effective, the medication should probably be changed. A typical dose is 50 mg.
SIDE EFFECTS
: Sedation, weight gain, a dry mouth, dizziness, and constipation. (See side effects for amitriptyline for more detail.) - N
ORTRIPTYLINE
(P
AMELOR
, A
VENTYL
)
When amitriptyline has been effective, but its side effects are too severe, doctors sometimes recommend nortriptyline because it causes less sedation; however, it is less effective and more expensive than amitriptyline. Nortriptyline is safer for the elderly than amitriptyline and the other older antidepressants because it has a relatively low risk of cardiac side effects. The new antidepressants, such as Prozac, however, may be even safer. Nortriptyline is also useful for children and adolescents.
TYPICAL DOSE: IO
mg to start, slowly increasing to 25 mg, sometimes to 100 mg, taken at night. Only available as capsules.
SIDE EFFECTS
: Similar to amitriptyline but less severe, including sedation (which decreases over time), weight gain, a dry mouth, constipation, or dizziness. Occasional anxiety or nervousness, but these side effects will quickly decrease. Less common side effects are depression, blurred vision, memory difficulties, and insomnia. - P
ROTRIPTYLINE
(V
IVACTIL
)
Protriptyline is often used when tension headaches are also a problem, or when nortriptyline’s side effects, such as sedation and weight gain, are too severe. It is not sedating and does not cause weight gain.
TYPICAL DOSE
: 2.5 mg to start each morning, increasing to 5 or 10 mg (sometimes even 30 or 50 mg, the typical doses prescribed for depression).
SIDE EFFECTS
: Nervousness. A dry mouth, constipation, and dizziness may occur. Insomnia (countered by taking it in the morning) occurs often, blurred vision and stomach upset less often. - D
ESIPRAMINE
(N
ORPRAMIN
)
Milder than other antidepressants, desipramine is useful if you are very sensitive to drug side effects. This medication is much more helpful, however, for chronic daily headaches than for migraines (see Chapter 9). - T
RIMIPRAMINE
(S
URMONTIL
)
Trimipramine is a good choice when amitriptyline no longer works or if its side effects are too severe. Though well tolerated compared to the other antidepressants, it is sedating. It is usually much more helpful for daily headaches than for migraines (see Chapter 9).
There are other antidepressants, known as MAO inhibitor antidepressants, such as phenelzine (Nardil), which are extremely effective, but their side effects, especially insomnia and weight gain, are severe compared with other antidepressants. Also, if you take an MAO inhibitor antidepressant, you will have to observe a very strict diet for safety reasons.
- M
ISCELLANEOUS
A
NTIDEPRESSANTS
(W
ELLBUTRIN
, R
EMERON
, E
FFEXOR
, S
ERZONE
)
Various other antidepressants are sometimes prescribed to prevent daily headache, migraine, or the anxiety and depression that often accompany chronic headaches.
Wellbutrin (bupropion) is a well-tolerated older antidepressant that rarely causes the sedation, weight gain, and sexual dysfunction often seen with other antidepressants. The usual dose is Wellbutrin SR 150 mg once or twice per day. While well tolerated and excellent for depression, Wellbutrin may not be as effective as some of the others for headache.
Remeron (mirtazapine) is a very effective antidepressant that is also useful for insomnia. The usual dose is 15 mg or 30 mg once per day. Sedation and weight gain may become major problems, however. Remeron is one of the very effective newer antidepressants.
Effexor (venlafaxine) is an excellent antidepressant that is occasionally useful for headache sufferers. The usual dose is 75 mg to 150 mg once per day. Nausea or dizziness may occur, but Effexor is generally well tolerated. Effexor has been a safe medication that has gained popularity for anxiety and depression in the past several years.
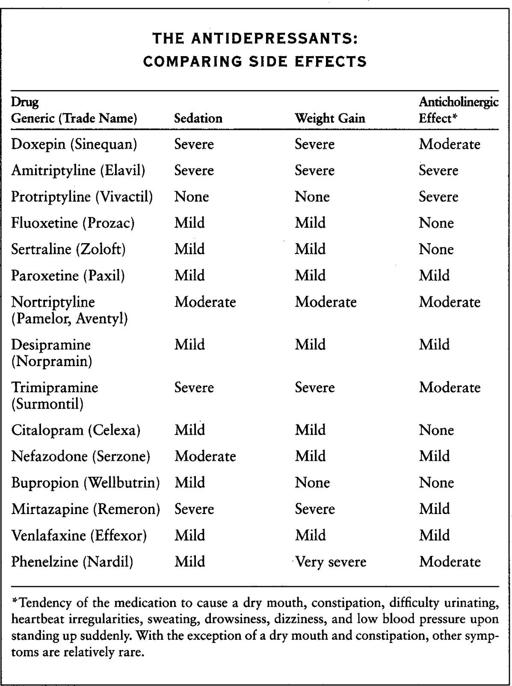
Serzone (nefazodone) is an effective newer antidepressant useful for insomnia as well. It is relatively mild, with typical antidepressant doses ranging from 200 mg to 450 mg. For headache sufferers, doctors typically recommend lower doses, such as 100 mg to 200 mg, at night. Serzone is relatively well tolerated, though sedation and weight gain may occur; occasionally helps headaches as well as anxiety or depression.
3. B
ETA
-B
LOCKERS
Beta-blockers, which prevent blood vessel dilation, are just as effective as amitriptyline or Depakote in preventing migraines, and often are used in combination with amitriptyline. Because they lower the pulse rate (which often gives people the sense of being slowed down), they may be prescribed with amitriptyline (or another antidepressant) to counter the antidepressant’s influence in increasing the heart rate.
If you have high blood pressure, taking a beta-blocker can help both the hypertension and the migraines. Beta-blockers also tend to help counter anxiety, but they may contribute to weight gain, depression, fatigue, higher cholesterol levels, diminished interest in sex, and problems concentrating. The side effects cease once you stop taking the drug.