Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine (103 page)
Read Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine Online
Authors: Marc Sabatine
Tags: #Medical, #Internal Medicine

INFLAMMATORY MARKER & AUTOANTIBODY TESTING
Inflammatory markers
(Mod Rheumatol 2009;19:469)
•
ESR
: indirect measure of inflammation (↑ RBC aggregation due to acute-phase proteins); slow to rise; ↑ w/ age, pregnancy, anemia, obesity •
CRP
: direct measure of inflammation (protein produced by liver, part of innate immune system); typically rises and falls before the ESR w/ treatment/resolution of process
Autoantibody testing
• ANA: screening test for Ab directed against extractable nuclear antigens (ENAs) found in autoimmune conditions, most useful in testing for connective tissue diseases • ENAs: proteins precipitated from spleen extracts; targets are generally of nuclear origin • Order ANA only when clinical suspicion for disease b/c nonspecific: 1:40 (low, 25–30% of healthy people); 1:80 (low
, 10–15% of healthy people); ≥1:160 (
, 5% of healthy). May be
in Pts prior to clin manifest (NEJM 2003;349:1526; Arthritis Res Ther 2011;13:1).
• Does not correlate well w/ disease activity, ∴ no clinical value in serial testing
• dsDNA and ENA antibodies (Ro/La/Smith/RNP) are highly specific for various CTD and can be used to further w/uANA in setting of clinical suspicion • RF and anti-CCP can be seen in CTD but are not specific
RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS (RA)
Definition & epidemiology
(
Lancet
2010;376:1094;
NEJM
2011;365:2205)
• Chronic, symmetric, debilitating and destructive inflammatory polyarthritis characterized by proliferative synovial tissue (pannus) formation in affected joints • Genetic (~50% of risk) & environmental factors (eg, smoking, silica dust exposure) • ↑ risk w/ shared epitope & smoke b/c gene–environment interaction (Ann Rheum Dis 2010;69:70) • Prevalence=1% adults; 5% of >70 y;
>70 y; to
to ratio=3:1; peak incidence 50–75 y
ratio=3:1; peak incidence 50–75 y
Clinical manifestations
(Medicine 2010;38:167)
• Usually insidious onset
pain
,
swelling
and impaired function of joints (typically PIPs, MCPs, wrists, knees, ankles, MTPs and cervical spine) with
morning stiffness
for ≥1 h • Typically polyarticular (60% small joints, 30% large joints, 10% both), may be monoarticular (knee, shoulder, wrist) early in course; nb, rheumatoid joints can become infected • Joint deformities:
ulnar deviation
,
swan neck
(MCP flexion, PIP hyperextension, DIP flexion),
boutonnière
(PIP flexion, DIP hyperextension),
cock-up deformities
(toes) •
C1–C2 instability
→ myelopathy, ∴✓ C-spine flex/ext films prior to elective intubation • Constitutional symptoms: low-grade fever, weight loss, malaise •
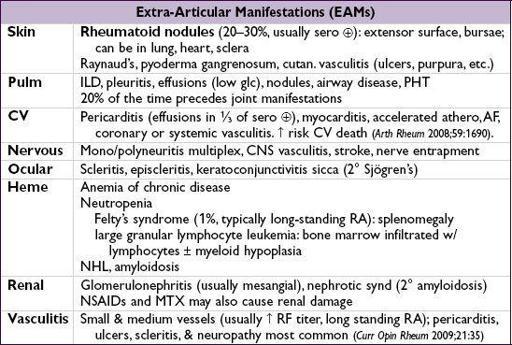
Extra-articular manifestations
(18–41% of Pts) can occur at any time; ↑ frequency in seropositive (RF or anti-CCP) (Autoimmun Rev 2011;11:123)
Laboratory & radiologic studies
•
RF
(IgM/IgA/IgG anti-IgGAb) in ~70% of Pts; also seen in other rheumatic diseases (SLE, Sjögren’s), infection (SBE, hepatitis, TB), types II & III cryo, 5% of healthy population •
Anti-CCP
(Ab to cyclic citrullinated peptide): in ~80% of Pts, similar Se (~70%), more Sp (>90%) than RF particularly for early RA (Arth Rheum 2009;61:1472); a/w increased joint damage and low remission rates • ~20% are seronegative (RF and anti-CCP negative) • ↑ ESR/CRP but nl in ~30%;ANA in ~15%; ↑ globulin during periods of active disease • Radiographs of hands and wrists: periarticular osteopenia, bone erosions, joint subluxation
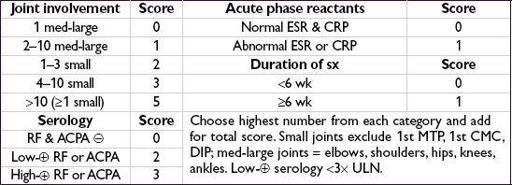
ACR/EULAR classification criteria
(
Arth Rheum
2010;62:2569)
• Use for Pts with ≥1 joint with synovitis not better explained by another disease • Summed score of ≥6 c/w RA