Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine (28 page)
Read Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine Online
Authors: Marc Sabatine
Tags: #Medical, #Internal Medicine

BOOK: Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine
3.08Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
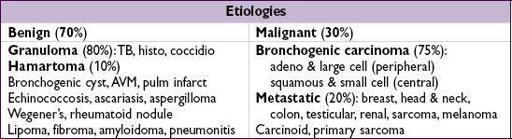
Initial evaluation
•
History
: h/o cancer, smoking, age (<30 y = 2% malignant, +15% each decade >30) •
CT
: size/shape, Ca
2+
, LAN, effusions, bony destruction,
compare w/ old studies
Ø Ca → ↑ likelihood malignant; laminated → granuloma; “popcorn” → hamartoma
• High-risk features for malignancy: ≥2.3 cm diameter, spiculated, >60 yo, >1 ppd current smoker, no prior smoking cessation (
NEJM
2003;348:2535)
Diagnostic studies
•
PET
: detects metab. activity of tumors, 97% Se & 78% Sp for malig. (esp. if >8 mm) also useful for surgical staging b/c may detect unsuspected mets (
JAMA
2001;285:914) useful in deciding which lesions to bx vs. follow w/ serial CT (
J Thor Oncol
2006;1:71) •
Transthoracic needle biopsy (TTNB)
: if tech. feasible, 97% will obtain definitive tissue dx (
AJR
2005;185:1294); if noninformative or malignant → resect •
Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery
(VATS): for percutaneously inaccessible lesions; highly sensitive and allows resection; has replaced thoracotomy • Transbronchial bx (TBB): most lesions too small to reliably sample w/o endobronchial U/S (
Chest
2003;123:604); bronch w/ brushings low-yield unless invading bronchus; navigational bronchoscopy w/ 70% yield, ↑ sens w/ larger nodules (
Chest
2012;142:385) • PPD, fungal serologies, ANCA
Management
(for solid SPN
>8 mm; if ≤8 mm, serial CT) (
Chest
2013;143:840)
•
Low risk
(<5%, see ref): serial CT (freq depending on risk); shared decision w/ Pt re: bx •
Intermediate risk
(5–60%): PET, if→ follow low-risk protocol; if
→ high-risk protocol •
High risk
(and surgical candidate): TBB, TTNB, or VATS → lobectomy if malignant •
Ground-glass nodules:
longer f/u b/c even if malignant can be slow-growing and PET
OBSTRUCTIVE SLEEP APNEA (OSA)
Definition and pathophysiology
• Repetitive pharyngeal collapse during sleep causing apnea (≥10 s) or hypopnea (airflow reduction) ± desaturation, arousals from sleep → daytime sleepiness • Apnea-hypopnea index = avg # apneas and hypopneas per hr of sleep • Sleep-induced loss of activity of pharyngeal dilator muscles → pharyngeal collapse → arousal → activation of sympathetic nervous system; phenotypes vary across OSA Pts • Apnea → negative intrathoracic pressure → ↑ preload, ↑ afterload → HTN, CV sequelae • Risk factors: obesity (present in 70%), male, age, alcohol, smoking, black race
Clinical manifestations
(
Lancet
2002;360:237;
Lancet Resp Med
2013;1:61)
• Snoring, witnessed apneas/gasping, daytime sleepiness •
Cardiovascular
: HTN (
JAMA
2012;307:2169); a/w ↑ risk of stroke and death (
NEJM
2005;353:2034) & possibly CAD & endothelial dysfxn (
AJRCCM
2001;163:19;
Circ
2008;117:2270) •
Neurocognitive
: ↓ cognitive performance, ↓ QoL, ↑ motor vehicle and work accidents (
NEJM
1999;340:847;
AJRCCM
2001;164:2031)
Diagnosis and treatment
•
Polysomnography
(sleep study); can do home-testing. If, trial of CPAP.
•
CPAP
: ↓↓ apnea/hypopnea, ↓ BP (
Lancet
2002;359:204), ↓ sleepiness, ↑ performance (
AJRCCM
2012;186:677), ↑ EF in Pts with CHF (
NEJM
2003;348:1233), ↓ metab syndrome (
NEJM
2011;365:2277), ↓ mortality after stroke (
AJRCCM
2009;180:36) • Oral appliances can prevent retroglossal collapse. Offer if refusing CPAP.
• Avoid alcohol and sedatives • Surgery (eg, uvulopalatopharyngoplasty, UPPP) of limited benefit (
Chest
1997;111:265)
INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE
WORKUP OF ILD
Rule out mimickers of ILD
•
Congestive heart failure
(✓ BNP, trial of diuresis) •
Infection
: viral, atypical bacterial, fungal, mycobacterial, parasitic •
Malignancy
: lymphangitic carcinomatosis, bronchoalveolar, leukemia, lymphoma
History and physical exam
• Occupational, travel, exposure (including tobacco), meds, FHx, precipitating event • Tempo (acute → infxn, CHF, hypersens pneumonitis, eos PNA, AIP, COP, drug-induced) • Extrapulmonary s/s (skin Ds, arthralgias/arthritis, clubbing, neuropathies, etc.)
Diagnostic studies
(see Appendix & Radiology inserts)
• CXR and
high-resolution chest CT
: reticular, nodular or ground glass pattern upper → coal, silicon, hypersens, sarcoid, TB, RA; lower → IPF, asbestos, scleroderma adenopathy → sarcoidosis, berylliosis, silicosis, malignancy, fungal infections pleural disease → collagen-vascular diseases, asbestosis, infections, XRT
• PFTs: ↓ D
L
CO (
early sign
), restrictive pattern (↓ volumes), ↓ P
a
O
2
(esp. w/ exercise); if also obstructive, consider sarcoid, LAM, silicosis • Serologies: ✓ ACE, ANA, RF, ANCA, anti-GBM, HIV
• Bronchoalveolar lavage: dx infxn, hemorrhage, eosinophilic syndromes, PAP
• Biopsy (transbronch, CT-guided, VATS, open) if no clear precipitant and w/u unrevealing
ETIOLOGIES OF ILD
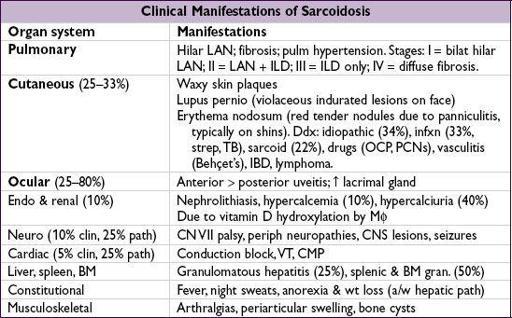
Sarcoidosis
(
NEJM
2007;357:2153;
JAMA
2011;305:391)
• Prevalence: African Americans, northern Europeans and females; onset in 3rd–4th decade • Pathophysiology: depression of cellular immune system peripherally, activation centrally
•
Löfgren’s syndrome
: erythema nodosum + hilar adenopathy + arthritis (good prognosis) • Diagnostic studies:
LN bx
→
noncaseating granulomas
+ multinucleated giant cells
18
FDG PET can be used to identify extent and potentially targets for dx bx ↑
ACE
(Se 60%, 90% w/ active dis., Sp 80%, falsein granulomatous diseases) • To assess extent: CXR, PFTs, full ophtho exam, ECG, CBC (lymphopenia, ↑ eos), Ca, 24-h urine for Ca, LFTs; ± Holter, echo, cardiac MRI, brain MRI, etc., based on s/s • Rx:
steroids
(eg, prednisone 20–40 mg/d) if sx or extrathoracic organ dysfxn (improves sx, but doesn’t Δ long-term course); hydroxychloroquine for extensive skin disease; anti-TNF, MTX, AZA, mycophenolate or cyclophosphamide for chronic/refractory disease • Prognosis: ~
2
/
3
spontaneously remit w/in 10 y (60–80% of stage I, 50–60% stage II, 30% stage III), w/ relapses uncommon; ~
1
/
3
have progressive disease
Iatrogenic
Other books
Tomorrow's ghost by Anthony Price
Reflections of the Wolf by Lori King
Shine by Jetse de Vries (ed)
Peggy Dulle - Liza Wilcox 05 - Till Death Do Us Part by Peggy Dulle
Love's Labyrinth by Anne Kelleher
Chimera by John Barth
The Thing on the Doorstep and Other Weird Stories by Lovecraft, H. P.
As You Are by Sarah M. Eden
Blind Love by Jasmine Bowen
Drowning in the East River by Kimberly Pierce