Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine (83 page)
Read Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine Online
Authors: Marc Sabatine
Tags: #Medical, #Internal Medicine

BOOK: Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine
9.72Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
•
Treatment
: monitor mild disease closely q3–6mo; for severe disease: fluconazole, itraconazole or amphotericin
Blastomycosis (
CID
2008;46:1801)
•
Endemic
: south central, SE and midwest U.S.
•
Clinical manifestations
Acute: 50% subclinical; cough, multilobar PNA; can progress to ARDS
Chronic pulm: cough, wt loss, malaise, CT w/ masses & fibronodular infiltrates
Disseminated: (25–40% of all but >> in immunosupp.): verrucous & ulcerated skin lesions, bone, & GU involvement; CNS rare unless immunosupp.
•
Treatment
: itraconazole (monitor levels); ampho B if severe, disseminated or immunosupp.
Aspergillosis
(
CID
2008;46:327;
NEJM
2009;360:1870)
•
ABPA
;
hypersensitivity pneumonitis
: see “Interstitial Lung Disease”
•
Aspergilloma
: usually in pre-existing cavity (from TB, etc.); most asx, but can lead to hemoptysis; sputum cxin <50%; CT → mobile intracavitary mass with air crescent
Rx: antifungals w/o benefit; embolization or surgery for persistent hemoptysis
•
Necrotizing tracheitis
: white necrotic pseudomembranes in Pts w/ AIDS or lung Tx •
Chronic necrotizing
: seen in COPD, mild immunosupp.; subacute sputum, fever, wt loss; CT: infiltrate ± nodule ± thick pleura; lung bx → invasion •
Invasive/disseminated
: seen if immunosupp. (neutropenia, s/p transplant, steroid Rx, AIDS esp. w/ steroids or neutropenia); s/s PNA w/
chest pain
&
hemoptysis
; CT: nodules, halo sign, air crescent sign; BAL + galactomannan; lung bx if dx inconclusive • Rx (necrotizing/invasive): voriconazole PO preferred to ampho; monitor serum levels
Zygomycetes
(eg,
Mucor
,
Rhizopus
)
•
Epidemiology
:
diabetes mellitus
(70%), heme malignancy, s/p transplant, chronic steroids, deferoxamine or iron overload, trauma, h/o voriconazole Rx or Ppx •
Clinical manifestations
:
rhinocerebral
= periorbital/forehead pain (more extensive than orbital cellulitis), ± fever (may appear nontoxic at first), exophthalmos, ↓ EOM, CNs (V > VII); nasal turbinates ± black eschar but exam can be quite nl. Also,
pulmonary
(PNA w/ infarct & necrosis);
cutaneous
(indurated painful cellulitis ± eschar);
GI
(necrotic ulcers).
•
Treatment
: Serial debridement + ampho (? + posaconazole). High mortality despite Rx.
Fungal diagnostics
•
Culture
:
Candida
grows in blood/urine Cx, but ↓ Se of BCx if deep tissue infection; others (eg,
Crypto
,
Histo
) ↓↓ Se of BCx; if suspect
Coccidio
alert lab
(biohazard)
•
Antibody detection
:
Histo
,
Blasto
,
Coccidio
,
Aspergillus
. Se variable (best for
Coccidio
).
•
Antigen detection
Histo urine/serum Ag
: Se of urine Ag 90% (serum 80%) if dissem; Sp limited by X-react
Crypto Ag
(serum, CSF): serum Ag >90% Se & Sp in invasive infxn, less for pulm only
1
,
3-
b
-D-glucan
: Se for many fungal infxns (
Candida, Aspergillus, Histo, Coccidio, Fusarium, Pneumocystis, Sporothrix
; but
not Crypto, Blasto, Mucor, Rhizopus
); not Sp
Galactomannan
: more specific for
Aspergillus
, but Se <50%. ↑ Se on BAL.
•
Biopsy
(ie, histopathology): nb, no grinding of tissue if Zygomycetes suspected
INFXNS IN IMMUNOSUPPRESSED HOSTS
Overview
• Many immunophenotypes, meds or systemic diseases predispose to infection
• Many Pts have ≥1 risk (eg, DM, ESRD, transplant, extremes of age); duration of risk varies
• The following is not an exhaustive list, but a delineation of common or classic etiologies
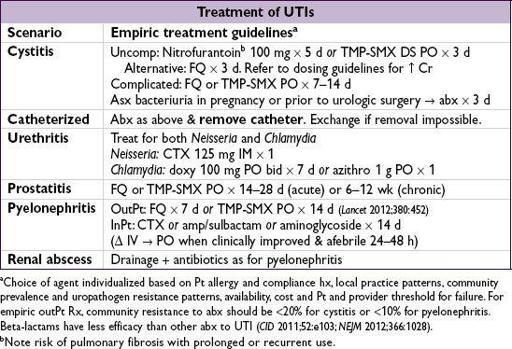
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS
Definitions
• Anatomic
lower
: urethritis, cystitis (superficial infection of bladder)
upper
: pyelonephritis (inflam of renal parenchyma), renal/perinephric abscess, prostatitis
• Clinical
uncomplicated
: cystitis in immunocompetent nonpregnant women w/o underlying structural or neurologic disease
complicated
: upper tract infection in women
or
any UTI in men or pregnant women
or
UTI with underlying structural disease or immunosuppression
Microbiology
• Uncomplicated UTI:
E. coli
(80%),
Proteus
,
Klebsiella
,
S. saprophyticus
(
CID
2004;39:75). In healthy, nonpregnant women, lactobacilli, enterococci, Group B strep and coag-neg staph (except
S. saprophyticus
) usually contaminants (
Annals
2012;156:ITC3).
• Complicated UTI:
E. coli
(30%), enterococci (20%),
PsA
(20%),
S. epi
(15%), other GNR
• Catheter-associated UTI:
yeast
(30%),
E. coli
(25%), other GNR, enterococci,
S. epi
• Urethritis:
Chlamydia trachomatis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Ureaplasma urealyticum, Trichomonas vaginalis, Mycoplasma genitalium
, HSV
•
S. aureus
: uncommon primary urinary pathogen in absence of catheter or recent instrumentation; ∴ consider bacteremia w/ hematogenous seeding
Clinical manifestations
•
Cystitis
:
dysuria
,
urgency
,
frequency
, hematuria, Δ in urine color/odor, suprapubic pain; fever usually
absent
. R/o vaginitis with symptoms of cystitis and urethritis.
•
Urethritis
: similar to cystitis except
urethral discharge
can be present •
Prostatitis
chronic
: similar to cystitis except
symptoms of obstruction
(hesitancy, weak stream)
acute
: perineal pain, fever, tenderness on prostate exam
•
Pyelonephritis
: fever, chills, flank or back pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea •
Renal abscess
(intrarenal, perinephric): identical to pyelonephritis w/
persistent fever despite appropriate antibiotics
Diagnostic studies
•
Urinalysis
:
pyuria
+
bacteriuria
± hematuria ± nitrites •
Urine Cx
(from clean-catch midstream or straight-cath specimen): obtain cx only if sx
Significant bacterial counts: typically ≥10
5
CFU/mL in women, ≥10
3
CFU/mL in men or catheterized Pts. Counts may vary depending on dilution & stage of infxn; interpret in context of symptoms and host.
Pyuria &UCx = sterile pyuria → urethritis, nephritis, renal tuberculosis, foreign body
• Blood cultures: obtain in febrile Pts; consider in complicated UTIs • DNA detection/cx for
C. trachomatis/N. gonorrhoeae
in high-risk Pts or sterile pyuria • If ? prostatitis: 1st void, midstream, prostatic expressage & postprostatic massage UCx • Abdominal CT: r/o abscess in Pts with pyelo who fail to defervesce after 72 h • Urologic w/u (renal U/S w/ PVR, abd CT, voiding cystography) if recurrent UTIs in men
SOFT TISSUE AND BONE INFECTIONS
CELLULITIS
Infection of superficial and deep dermis and subcutaneous fat
Microbiology & clinical
(
NEJM
2004;350:904;
CID
2005;41:1373)
• Primarily strep and staph, including MRSA; may include GNRs in diabetics/immunosupp.
•
Community-acquired MRSA (CA-MRSA)
(
NEJM
2005;352:1485 & 2006;355:666)
Other books
Cum For Bigfoot 11, Lena's Story by Virginia Wade
It Could Happen Again (Zulu Spectre) by Aliyah Burke
Holly's Heart Collection Two by Beverly Lewis
Thunder Road by Ted Dawe
A Fortune's Children's Christmas by Lisa Jackson, Linda Turner, Barbara Boswell
Cold Ennaline by RJ Astruc
Key Trilogy by Nora Roberts
The Lucky One (Brethren Of The Coast #6) by Barbara Devlin
Such Good Girls by R. D. Rosen
Sisters of the Heart - 03 - Forgiven by Shelley Shepard Gray