Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis (611 page)
Authors: Mary A. Williamson Mt(ascp) Phd,L. Michael Snyder Md

BOOK: Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis
8.32Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
D = decreased; I = increased; N = normal.
TABLE 13–3. Illustrative Serum Electrolyte Values in Various Conditions
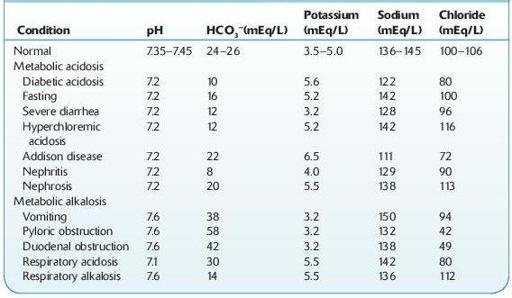
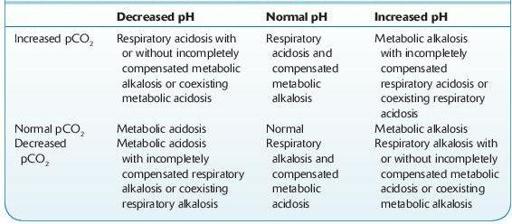
TABLE 13–4. Summary of Pure and Mixed Acid–Base Disorders
Data from Friedman HH.
Problem-Oriented Medical Diagnosis
, 3rd ed. Boston, MA: Little, Brown; 1983.
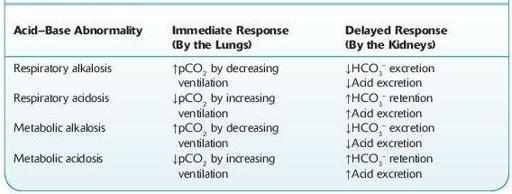
TABLE 13–5. Immediate and Delayed Compensatory Response to Acid–Base Disturbances
↑, increases; ↓, decreases.
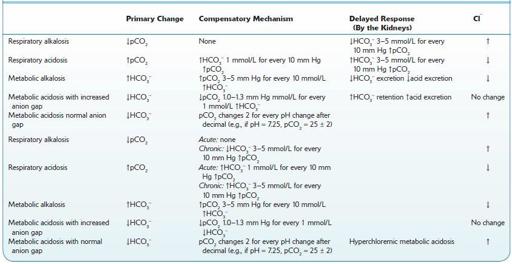
TABLE 13–6. Primary Change, and Compensatory Mechanisms in Delayed Response to, and Chloride Level in AcidBase Disturbances
↑, increased;↓, decreased.
RESPIRATORY ALKALOSIS
Respiratory alkalosis is defined as a decreased pCO
2
of <38 mm Hg.
Caused by Hyperventilation
CNS disorders (e.g., infection, tumor, trauma, CVA, anxiety–hyperventilation)
Hypoxia (e.g., high altitudes, ventilation–perfusion imbalance, PE)
Cardiovascular (e.g., CHF, hypotension)
Pulmonary disease (e.g., pneumonia, pulmonary emboli, asthma, pneumothorax)
Drugs (e.g., salicylate intoxication, methylxanthines, β-adrenergic agonists)
Metabolic (e.g., acidosis [diabetic, renal, lactic], Cirrhosis, liver failure)
Others (e.g., fever, pregnancy, gram-negative sepsis, pain)
Other books
Counseling Through Your Bible Handbook by June Hunt
Scandalous by Melanie Shawn
Arson by Estevan Vega
The Gift of Numbers by Yôko Ogawa
The Homicide Hustle by Ella Barrick
The Convenient Marriage by Georgette Heyer
Courage: Overcoming Fear and Igniting Self-Confidence by Debbie Ford
Ocho casos de Poirot by Agatha Christie
Heidi by Johanna Spyri
1 Death by Chocolate by Carol Lee