Watkin Tench's 1788 (33 page)

But even this heat was judged to be far exceeded in the latter end of the following February, when the north-west wind again set in, and blew with great violence for three days. At Sydney, it fell short by one degree of what I have just recorded: but at Rose Hill, it was allowed, by every person, to surpass all that they had before felt, either there or in any other part of the world. Unluckily they had no thermometer to ascertain its precise height. It must, however, have been intense, from the effects it produced. An immense flight of bats driven before the wind, covered all the trees around the settlement, whence they every moment dropped dead or in a dying state, unable longer to endure the burning state of the atmosphere.
â
Nor did the
perroquettes
, though tropical birds, bear it better.
â â
The ground was strewed with them in the same condition as the bats.
Were I asked the cause of this intolerable heat, I should not hesitate to pronounce that it was occasioned by the wind blowing over immense deserts, which, I doubt not, exist in a north-west direction from Port Jackson,
and not from fires kindled by the natives
. This remark I feel necessary, as there were methods used by some persons in the colony, both for estimating the degree of heat and for ascertaining the cause of its production, which I deem equally unfair and unphilosophical. The thermometer, whence my observations were constantly made, was hung in the open air, in a southern aspect, never reached by the rays of the sun, at the distance of several feet above the ground.
My other remarks on the climate will be short. It is changeable beyond any other I ever heard of; but no phenomena sufficiently accurate to reckon upon, are found to indicate the approach of alteration. Indeed, for the first eighteen months that we lived in the country, changes were supposed to take place more commonly at the quartering of the moon than at other times. But lunar empire afterwards lost its credit. For the last two years and a half of our residing at Port Jackson, its influence was unperceived. Three days together seldom passed without a necessity occurring for lighting a fire in an evening. A
habit d'ete
, or a
habit de demi sáison
,
â â â
would be in the highest degree absurd. Clouds, storms and sunshine pass in rapid succession. Of rain, we found in general not a sufficiency, but torrents of water sometimes fall. Thunderstorms, in summer, are common and very tremendous, but they have ceased to alarm, from rarely causing mischief. Sometimes they happen in winter. I have often seen large hailstones fall. Frequent strong breezes from the westward purge the air. These are almost invariably attended with a hard clear sky. The easterly winds, by setting in from the sea, bring thick weather and rain, except in summer, when they become regular sea-breezes. The
aurora australis
is sometimes seen, but is not distinguished by superior brilliancy.
To sum up: notwithstanding the inconveniences which I have enumerated, I will venture to assert in few words that no climate hitherto known is more generally salubrious,
**
or affords more days on which those pleasures which depend on the state of the atmosphere can be enjoyed, than that of New South Wales. The winter season is particularly delightful.
The leading animal production is well known to be the kangaroo. The natural history of this animal will, probably, be written from observations made upon it in England, as several living ones of both sexes have been brought home. Until such an account shall appear, probably the following desultory observation may prove acceptable.
The genus in which the kangaroo is to be classed I leave to better naturalists than myself to determine. How it copulates, those who pretend to have seen disagree in their accounts: nor do we know how long the period of gestation lasts. Prolific it cannot be termed, bringing forth only one at a birth, which the dam carries in her pouch wherever she goes until the young one be enabled to provide for itself; and even then, in the moment of alarm, she will stop to receive and protect it. We have killed she-kangaroos whose pouches contained young ones completely covered with fur and of more than fifteen pounds weight, which had ceased to suck and afterwards were reared by us. In what space of time it reaches such a growth as to be abandoned entirely by the mother, we are ignorant. It is born blind, totally bald, the orifice of the ear closed and only just the centre of the mouth open, but a black score, denoting what is hereafter to form the dimension of the mouth, is marked very distinctly on each side of the opening. At its birth, the kangaroo (notwithstanding it weighs when full grown 200 pounds) is
not so large as a half-grown mouse
. I brought some with me to England even less, which I took from the pouches of the old ones. This phenomenon is so striking and so contrary to the general laws of nature, that an opinion has been started that the animal is brought forth not by the pudenda, but descends from the belly into the pouch by one of the teats which are there deposited. On this difficulty, as I can no throw no light, I shall hazard no conjecture. It may, however, be necessary to observe that the teats are several inches long and capable of great dilatation. And here I beg leave to correct an error which crept into my former publication wherein I asserted that, âthe teats of the kangaroo never exceed two in number.' They sometimes, though rarely, amount to four. There is great reason to believe that they are slow of growth and live many years. This animal has a clavicle, or collarbone, similar to that of the human body. The general colour of the kangaroo is very like that of the ass, but varieties exist. Its shape and figure are well known by the plates which have been given of it. The elegance of the ear is particularly deserving of admiration. This far exceeds the ear of the hare in quickness of sense and is so flexible as to admit of being turned by the animal nearly quite round the head, doubtless for the purpose of informing the creature of the approach of its enemies, as it is of a timid nature and poorly furnished with means of defence; though when compelled to resist, it tears furiously with its forepaws, and strikes
forward
very hard with its hind legs. Notwithstanding its unfavourable conformation for such a purpose, it swims strongly; but never takes to the water unless so hard pressed by its pursuers as to be left without all other refuge. The noise they make is a faint bleat, querulous, but not easy to describe. They are sociable animals and unite in droves, sometimes to the number of fifty or sixty together; when they are seen playful and feeding on grass, which alone forms their food. At such time they move gendy about like all other quadrupeds, on all fours; but at the slightest noise they spring up on their hind legs and sit erect, listening to what it may proceed from, and if it increases they bound off on those legs only, the fore ones at the same time being carried close to the breast like the paws of a monkey; and the tail stretched out, acts as a rudder on a ship. In drinking, the kangaroo laps. It is remarkable that they are never found in a fat state, being invariably lean. Of the flesh we always eat with avidity, but in Europe it would not be reckoned a delicacy. A rank flavour forms the principal objection to it. The tail is accounted the most delicious part, when stewed.
Hitherto I have spoken only of the large, or grey kangaroo, to which the natives give the name of
patagarà n
.
***
But there are (besides the kangaroo-rat) two other sorts. One of them we called the red kangaroo, from the colour of its fur, which is like that of a hare, and sometimes is mingled with a large portion of black: the natives call it
bà garay
.
â â â â
It rarely attains to more than forty pounds weight. The third sort is very rare, and in the formation of its head resembles the opossum. The kangaroo-rat is a small animal, never reaching, at its utmost growth, more than fourteen or fifteen pounds, and its usual size is not above seven or eight pounds. It joins to the head and bristles of a rat the leading distinctions of a kangaroo, by running when pursued on its hind legs only, and the female having a pouch. Unlike the kangaroo, who appears to have no fixed place of residence, this little animal constructs for itself a nest of grass, on the ground, of a circular figure, about ten inches in diameter, with a hole on one side for the creature to enter at; the inside being lined with a finer sort of grass, very soft and downy. But its manner of carrying the materials with which it builds the nest is the greatest curiosity: by entwining its tail (which, like that of all the kangaroo tribe, is long, flexible and muscular) around whatever it wants to remove, and thus dragging along the load behind it. This animal is good to eat; but whether it be more prolific at a birth than the kangaroo, I know not.
The Indians sometimes kill the kangaroo; but their greatest destroyer is the wild dog,
****
who feeds on them. Immediately on hearing or seeing this formidable enemy, the kangaroo flies to the thickest cover, in which, if he can involve himself, he generally escapes. In running to the cover, they always, if possible, keep in paths of their own forming, to avoid the high grass and stumps of trees which might be sticking up among it to wound them and impede their course.
Our methods of killing them were but two; either we shot them, or hunted them with greyhounds. We were never able to ensnare them. Those sportsmen who relied on the gun seldom met with success, unless they slept near covers, into which the kangaroos were wont to retire at night, and watched with great caution and vigilance when the game, in the morning, sallied forth to feed. They were, however, sometimes stolen in upon in the daytime; and that fascination of the eye, which has been by some authors so much insisted upon, so far acts on the kangaroo that if he fix his eye upon anyone, and no other object move at the same time, he will often continue motionless, in stupid gaze, while the sportsman advances with measured step towards him, until within reach of his gun. The greyhounds for a long time were incapable of taking them; but with a brace of dogs, if not near cover a kangaroo almost always falls, since the greyhounds have acquired by practice the proper method of fastening upon them. Nevertheless the dogs are often miserably torn by them. The rough wiry greyhound suffers least in the conflict, and is most prized by the hunters.
Other quadrupeds, besides the wild dog, consist only of the flying squirrel, of three kinds of opossums and some minute animals, usually marked by the distinction which so peculiarly characterises the opossum tribe. The rats, soon after our landing, became not only numerous but formidable, from the destruction they occasioned in the stores. Latterly they had almost disappeared, though to account for their absence were not easy. The first time Colbee saw a monkey, he called
wurra
(a rat), but on examining its paws he exclaimed with astonishment and affright,
mulla
(a man).
At the head of the birds the cassowary, or emu, stands conspicuous. The print of it which has already been given to the public is so accurate for the most part, that it would be malignant criticism in a work of this kind to point out a few trifling defects.
Here again naturalists must look forward to that information which longer and more intimate knowledge of the feathered tribe than I can supply, shall appear. I have nevertheless had the good fortune to see what was never seen but once, in the country I am describing, by Europeansâa hatch, or flock, of young cassowaries with the old bird.
â â â â â
I counted ten, but others said there were twelve. We came suddenly upon them, and they ran up a hill exactly like a flock of turkeys, but so fast that we could not get a shot at them. The largest cassowary ever killed in the settlement, weighed ninety-four pounds. Three young ones, which had been by accident separated from the dam, were at once taken and presented to the governor. They were not larger than so many pullets, although at first sight they appeared to be so from the length of their necks and legs. They were very beautifully striped, and from their tender state were judged to be not more than three or four days old. They lived only a few days.
A single egg, the production of a cassowary, was picked up in a desert place, dropped on the sand, without covering or protection of any kind. Its form was nearly a perfect ellipsis; and the colour of the shell a dark green, full of little indents on its surface. It measured eleven inches and a half in circumference, five inches and a quarter in height, and weighed a pound and a quarter. Afterwards we had the good fortune to take a nest. It was found by a soldier in a sequestered solitary situation, made in a patch of lofty fern about three feet in diameter, rather of an oblong shape and composed of dry leaves and tops of fern stalks, very inartificially put together. The hollow in which lay the eggs, twelve in number, seemed made solely by the pressure of the bird. The eggs were regularly placed in the following position.
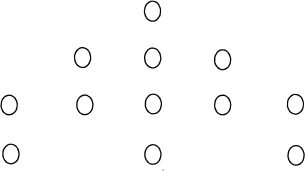
*
Look at the journal which describes the expedition in search of the river, said to exist to the southward of Rose Hill. At the time we felt that extraordinary degree of cold, we were not more than six miles south-west of Rose Hill, and about nineteen miles from the sea coast. When I mentioned this circumstance to Colonel Gordon, at the Cape of Good Hope, he wondered at it; and owned that, in his excursions into the interior parts of Africa, he had never experienced anything to match it: he attributed its production to large beds of nitre, which he said must exist in the neighbourhood.