Blue Angel (26 page)
Authors: Donald Spoto

W
ITH
G
ARDEN
COMPLETE AT THE END OF
J
UNE
, D
IE
trich was therefore again free to accept another offer, which she quickly did when Alexander Korda (who had employed her a decade earlier in Germany) cabled from England, where he had settled and established a production company. And so in early July, with twenty trunks, thirty handbags, two maids and Maria, Dietrich boarded the
Normandie
in New York. “It isn’t that I don’t like America,” she had told the press, saying yet again (as she had in 1933) that she might remain abroad permanently. “It is just that America is not my country.” After leaving Maria with Sieber and Tamara in Paris, she proceeded to London to begin filming
Knight Without Armour
, for which she earned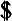 450,000. In 1936, Marlene Dietrich was the highest paid woman in the world.
450,000. In 1936, Marlene Dietrich was the highest paid woman in the world.
At a press conference at the Dorchester Hotel, she met with Korda, French director Jacques Feyder and her co-star Robert Donat. Filming was to begin before the end of July, but Donat’s chronic asthma turned suddenly severe. After a six-week delay, Korda—overburdened by high actors’ salaries and the costs of maintaining numerous exterior sets at Denham Studios—understandably considered dismissing Donat and radically reducing his role for another actor. But Dietrich was adamant. Although a dozen men could have easily assumed the role and she had no reason to concern herself with his career, she informed Korda that she would not remain with the project if he dismissed the ailing Donat—even if her own part were to improve in the bargain. Her gesture was duly noted and appreciated by Donat, his wife and family, and admired by her colleagues on
Knight Without Armour
. Throughout production, she was constantly alert for Donat’s well-being, covering him with her own fur coat while they waited in the autumn chill for a camera setup.
But the film could not have been saved by the healthiest men in England. As a widowed Russian countess who flees the 1917 revolution with the help of a British spy, she was required to do very little but pose prettily, swathed in chiffon or bathing provocatively as soap bubbles slowly burst in the tub. She was at first delighted to work with Feyder, a respected director who observed that
she only makes “Marlene Dietrich films,” and accordingly she is concerned with one thing only: that this will be a Marlene Dietrich picture. Her image, her face, her costumes—in her estimation, only these count. Her technical experience enables her to verify if the light on her face is positioned as she wishes. You can usually hear her ordering the electricians around: “Put two more lamps on the right . . . reposition the key light higher behind me.”
Feyder also resented her peculiar notions about costumes, which refused to consider the script, the setting or the character’s situation:
“It all has to serve Dietrich—that’s the sole reality—and if she does or wears something anachronistic, well, then, you just have to change the script to conform to her wishes.” He resented her manipulations, her subtle seductions of whoever might serve her best at a particular moment during production. “The reputation she has for cooperation is remarkable,” Feyder considered, “for that’s really the height of her illusion. When you see the finished film you realize she’s had her own way in just about everything. Marlene Dietrich indeed has
so
much charm.”
Cinematographer Harry Stradling likewise recalled that, to ensure her best appearance, Dietrich once again demanded a full-length mirror beside the camera, so that if she felt too much light on her arms, or if her shoulders caught too much from a certain arc, she could instruct Stradling accordingly.
*
Preparing for her bathtub scene, Dietrich had informed only her dresser that she would perform nude (without the customary flesh-covered bathing suit invisible to the camera). Production workers are not easily astonished men, but there was some commotion that autumn day when Dietrich arrived on the set, tossed aside her robe and (as a witness recalled) expertly “slipped and sprawled, spread-eagled naked before the camera crew.” She laughed, winked at her colleagues and went on with the scene. It was then learned that, as she had known in advance, a correspondent for
Time
was present. On November 30, 1936, Dietrich (clothed and with a distinctly Mona Lisa smile) graced the magazine’s cover. Onscreen, her bubble bath was the sole moment of interest in a picture that otherwise induced in viewers only a stupefying lethargy.
But there was also a mild disturbance when the German actress Mady Soyka, wife of Dietrich’s former Berlin agent, visited her dressing room; with her was journalist Willi Frischauer, who years later recalled the meeting. Soyka had been sent by Joseph Goebbels (Hitler’s propaganda minister) with an offer of fifty thousand British pounds, payable tax-free and in any currency, if Dietrich would return to Germany for just a month to make one picture. “You can have anything you want,” Soyka said. “Anything!”
But despite her widely quoted comment that “America is not my country,” Dietrich had not implied that Germany was. Compatriots by the score in the United States, France and England had been telling her what the press had now begun to confirm, and so—brilliantly exploiting her trademark brand of aloof disdain—she cast a long, appraising, head-to-toe stare at Mady Soyka and then replied flatly, “This comes as a great surprise,” referring no doubt to the condemnations of her that had become commonplace in the German press since the time of
Song of Songs
. Soyka increased the pressure: “There will be an immediate reversal of the press campaign against you. The German public will be suitably prepared for your return.”
The political implications of this apparently casual meeting were enormous, but Dietrich—who knew she was being used like the 1936 summer Olympic games in Germany, for propaganda and prestige—would have none of it. “Darling,” she said sweetly, spinning a fantastic fiction for Mady Soyka, “how nice of you to bring me this marvelous offer. What a pity I cannot accept it at the moment. You see, I am under contract for the next two years, which takes us to the end of 1938. Then I am committed to do a play on Broadway in 1939. Shall we not return to the idea perhaps in 1940 or 1941?”
Dietrich’s visitor departed swiftly. When the Nazis later occupied Paris during the war, Soyka, a great beauty celebrated for her naturally golden hair, managed a café on the Champs-Elysées. But some members of the French Resistance were offended when she ostentatiously wore gems and bracelets that had once belonged to Parisian Jews who subsequently vanished. One day in 1942, so did she: it was later determined that the Resistance had whisked her off, coiffed and bejewelled, to a swift, quiet execution as retribution for her spying on French Jews.
D
ELAYS DURING
K
NIGHT
W
ITHOUT
A
RMOUR
DID
not leave Dietrich idle. In her suite at Claridge’s she welcomed interviewers and in midsummer returned briefly to Paris for fittings with couturiers. But most of her private time in London for the remainder of 1936 and into early 1937 was spent in the company of
the American actor Douglas Fairbanks, Jr. Son of the spirited silent-screen star, he was pursuing a movie career of his own, mostly in England, where his social connections enabled him to enjoy the company of aristocrats, statesmen and even the confidence of some members of the royal family—among them George, Duke of Kent (brother of the still uncrowned King Edward VIII) and his wife, Princess Marina of Greece. A tall, articulate, witty and strikingly handsome man, Fairbanks was then divorced from Joan Crawford and had (as he described in his memoirs) a vivid and busy romantic life—until he met Marlene Dietrich that July, at a dinner party given by Alexander Korda. Only years after their last meeting did he learn she was eight years older than he.
Soon after the evening at Korda’s, Fairbanks invited Dietrich to the premiere of his new film,
Accused;
she accepted, bringing along Rudi and Tamara, who were then visiting in London. At first baffled by the openly unconventional arrangement, Fairbanks quickly learned that the Siebers were, as he said years later, “really like brother and sister. It had, Marlene said, been a marriage only long enough for Maria to have been conceived, but they remained good friends and he managed her finances.” Within a week of that evening, Fairbanks and Dietrich were spending most nights together, alternately in her suite and his new penthouse flat, very near Claridge’s, at 20 Grosvenor Square, Mayfair.
At first, Fairbanks assumed their affair was “only her passing fancy”—doubtless a reaction not only to her obvious independence but also to the shrine on her bedside table, with a votive candle ever burning before a photo of John Gilbert. These items remained in plain view for over two months, as Dietrich persisted (so said Fairbanks) in “maintaining the fictitious drama that John Gilbert died because of her,” an assertion stoutly rejected by Gilbert’s family. The memorabilia were temporarily packed away only when she abandoned her hotel suite and took a small flat on the floor below Fairbanks in Grosvenor Square. There the relationship thrived without the awkward hindrances of Claridge’s, where, on mornings after a formal event he had attended with Dietrich, Fairbanks had to descend a rear fire escape in full-dress tailcoat.
Although, as Fairbanks later admitted, he and Dietrich were not
really in love with each other, it was “a relationship of more sophisticated intensity” than he had hitherto known. She was not only an ardent mistress; she also responded empathetically to the strained relationship between Fairbanks and his famous, powerful and somewhat intimidating father who “rarely seemed to be more than vaguely aware of my presence . . . I failed to win any real affection from him.”
Douglas Fairbanks, Jr., was, therefore, not only an appealing and socially desirable companion she could respect but also one, like von Sternberg, to whom she could extend the kind of nurturing solace that was at once manipulative, parental and even somewhat detached. While neither as isolated as von Sternberg nor as wounded as Gilbert, Fairbanks was, at twenty-six, emotionally vulnerable after the failure of his marriage to the formidable Joan Crawford. He was nevertheless serious about his career and young enough to be responsive to an internationally famous woman who had raised tender domination to the level of a fine art. In his memoirs, Fairbanks described his mother, the redoubtable Anna Beth Sully, as a woman who “longed for—but seldom got—the kind of smothering devotion that she lavished on her own loved ones.” His subsequent attraction to two equally strong women (Crawford and Dietrich) is not hard to understand.
Perhaps because
Knight Without Armour
had introduced her to a few Russian words (or because it was the name of the Duke of Kent’s German shepherd), Dietrich gave Fairbanks the nickname “Dushka,” a term of endearment. This was not only an effective code-name for messages and notes; she also had it engraved on expensive gifts for him, among them a gold wristwatch. On weekends during film production, the lovers regularly entertained for cocktails and dinner—unless they had accepted an invitation out of town, to Lady Morvyth’s country house in Hampshire, for example, or to Coppins, the Kents’ residence in Buckinghamshire. Despite widespread economic hardship, 1936 was for the upper classes perhaps the zenith of England’s age of lustrous (if somewhat fanciful) social elegance. Dietrich, always magnificent to escort, was also enough of a Prussian traditionalist to be a zealous supporter of the English monarchy, a posture which could only have further endeared
this glamorous star to her fashionable new friends. (Some, to her dismay, were as ardent in their support of Germany as she was of England.)
So much was Dietrich a royalist, in fact, that she was roused to dramatic action by the rumors of Edward VIII’s imminent abdication for the sake of Wallis Simpson in early December 1936. Distressed that the king might indeed defy the advice of his ministers and the hopes of his people, she was suddenly convinced that she—and only she—could prevent history from taking a tragic course. The first week of December, Dietrich summoned her liveried chauffeur and, determined to dissuade the king (by seducing him, if necessary) from abandoning the throne for Mrs. Simpson, she motored down to Fort Belvedere in her enormous limousine. But her arrival in such grand style was a signal to the ever present press as well as the police, and despite her altercation with the guards, Dietrich could not gain admission. Within days, Edward broadcast his news to the world—an event which, she was persuaded, would never have occurred had she been permitted a meeting with His Majesty.
As Fairbanks recalled, Dietrich basked in her new aristocratic connections and began to exaggerate her own pedigree. During that season, she even seriously weighed the potential advantages of adopting British citizenship. She was, however, embarrassed by the fact that her uncle had commanded the first Zeppelin raid over London during the war, and she feared this being known. Not so her romance with Fairbanks. With the shrewdness of a Hollywood publicist, she refused ever to confirm the affair, then or later; on the contrary, she always allowed her relationships (even those that remained platonic) to be the more excitingly surmised.