Breast Imaging: A Core Review (23 page)
Read Breast Imaging: A Core Review Online
Authors: Biren A. Shah,Sabala Mandava
Tags: #Medical, #Radiology; Radiotherapy & Nuclear Medicine, #Radiology & Nuclear Medicine

A. Enhancement of the pectoralis muscle
B. No intervening fat plane between the mass and muscle
C. There is no predictive criteria.
D. Vessels extending from the mass into muscle
76
Which of the following statements is correct about recurrent breast cancer?
A. Local recurrence rate after breast conservation therapy is 10% to 20%.
B. Most cases of recurrence occur within the first 2 years of treatment.
C. MRI offers an advantage over other modalities in assessing recurrence.
D. On MRI, physiologic enhancement at the surgical site is seen up to 2 months after surgery.
77
A 39-year-old female with a strong family history of breast cancer presents for diagnostic mammogram for left breast pain. Based on the images, what is the most likely diagnosis?
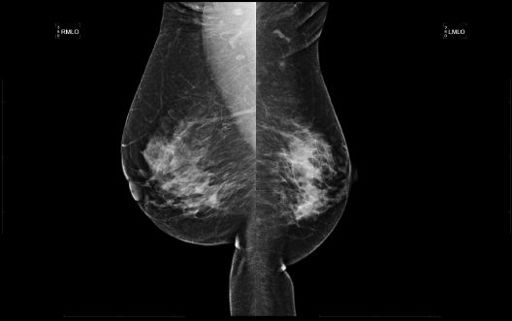
A. Transverse rectus abdominis myocutaneous (TRAM) flap reconstruction
B. Poland syndrome
C. Mastectomy
D. Reduction mammoplasty
78
The following images from a contrast-enhanced breast MRI are provided. In the central right breast, there is clumped nonmass enhancement. Kinetic assessment of the nonmass enhancement using CAD (computer-aided detection) processing software demonstrates which type of curve?
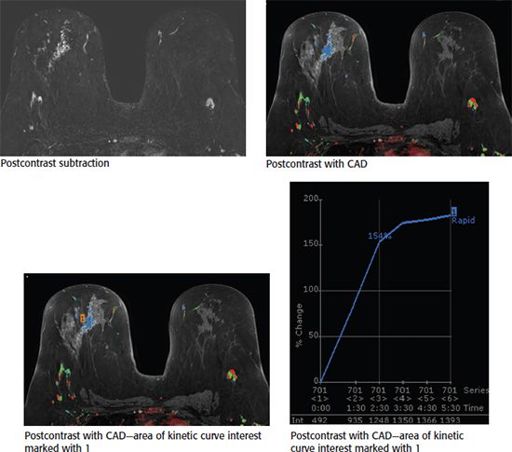
A. Initial slow, delayed washout
B. Initial rapid, delayed persistent
C. Initial rapid, delayed plateau
D. Initial rapid, delayed washout
E. Initial slow, delayed plateau
79
The most common malignant breast mass in a pregnant and postpartum patient is:
A. invasive medullary carcinoma
B. invasive lobular carcinoma
C. invasive ductal carcinoma
D. invasive mucinous carcinoma
E. invasive tubular carcinoma
80
A 55-year-old female was recently diagnosed with an invasive ductal carcinoma of two masses in the left breast. Mass A is 3.1 cm in greatest diameter and is located in the left upper outer quadrant at posterior depth. Mass B is 4 cm in greatest diameter and located in the left lower inner quadrant at middle depth. Which statement is correct?
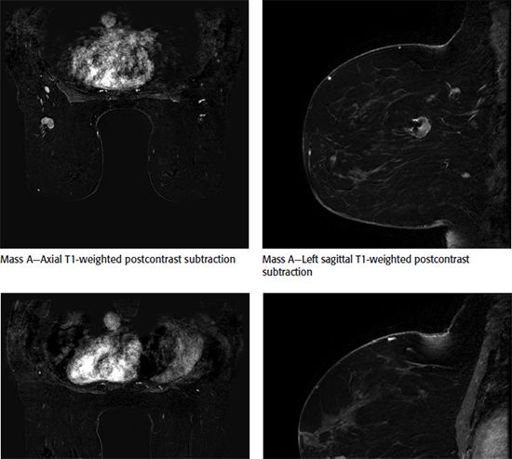
A. The patient is a candidate for whole-breast radiation therapy.
B. The patient is a candidate for breast conserving surgery.
C. The findings are suspicious for multifocal invasive breast cancer on MRI.
D. The findings are suspicious for multicentric invasive breast cancer on MRI.
81
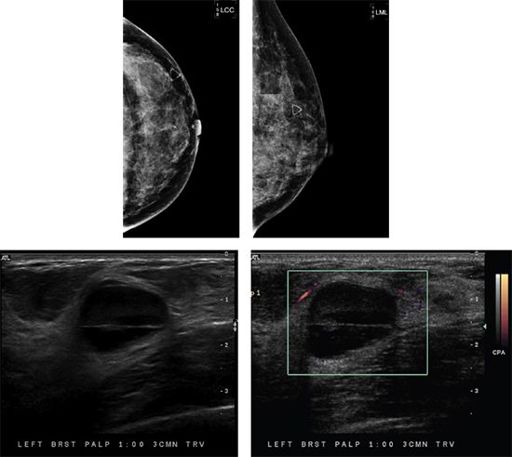
81a
A 34-year-old female presents with a palpable lump in her left breast. Based on the mammogram and ultrasound images, which one of the following is the most appropriate BI-RADS category assessment?
A. BI-RADS 1
B. BI-RADS 2
C. BI-RADS 3
D. BI-RADS 4
81b
Based on the ultrasound images, what is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Hamartoma
B. Galactocele
C. Intramammary lymph node
D. Lipoma
E. Fat necrosis
82
A 41-year-old female presents with a palpable lump in her left breast. Based on the images, what is the most appropriate management?
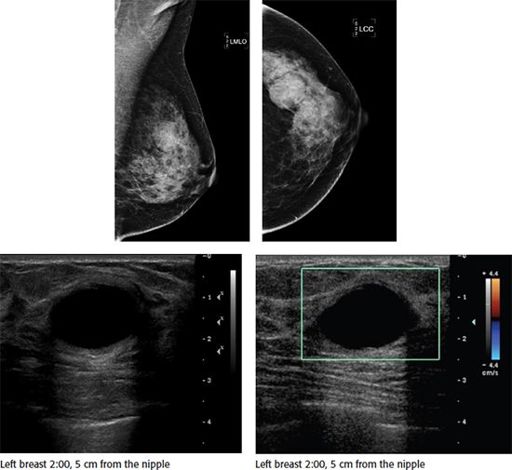
A. No further evaluation
B. Cyst aspiration for diagnosis
C. Core needle biopsy
D. Antibiotic therapy
83
The most common mammographic finding of pregnancy associated breast cancer is:
A. microcalcifications
B. edema
C. architectural distortion
D. mass
E. axillary adenopathy
84
Shown is a spot magnification view of axillary lymph nodes along with ultrasound images taken of the left axillary region. These lymph nodes were seen on ultrasound as well. If this is a new finding in a patient that has a history of ipsilateral breast cancer, what is the BI-RADS category assessment?
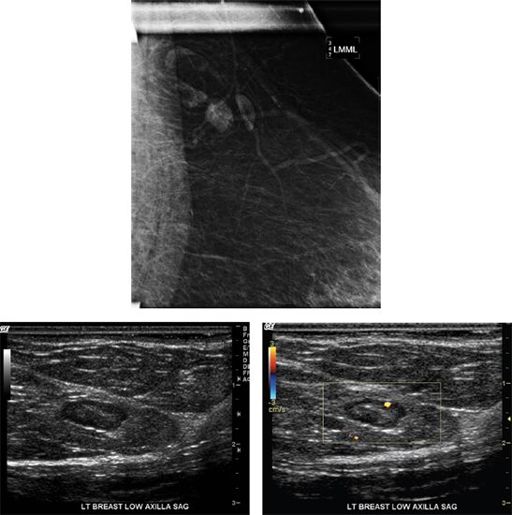
A. BI-RADS 2
B. BI-RADS 3
C. BI-RADS 4
D. BI-RADS 6
85
Shown is a breast MRI image demonstrating a mass in the right breast at 7 o’clock at a middle depth. The time–intensity kinetic curve showed a type I curve. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step?
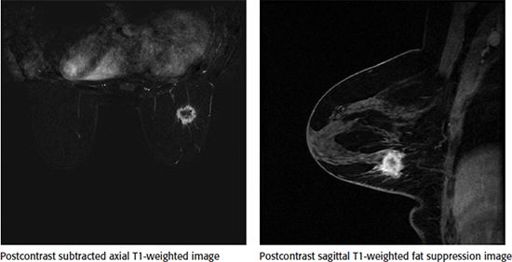
A. Recommend a follow-up 6-month breast MRI to document stability.
B. The mass should be categorized as BI-RADS 2, and continued risk-appropriate screening should be recommended.
C. Biopsy should be performed despite benign kinetics.
D. The study is limited due to suboptimal technique and should be repeated.
86
Based on the diagnostic ultrasound images, which one of the following is the most appropriate BI-RADS category assessment?
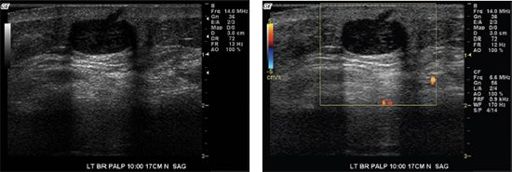
Other books
Prisoners of the Williwaw by Ed Griffin
Sophie's Encore by Nicky Wells
The Goodbye Girl by Angela Verdenius
For Such a Time by Breslin, Kate
Rich Promise by Ashe Barker
Labor of Love by Rachel Hawthorne
A Safe Place for Dying by Jack Fredrickson
February Fever by Jess Lourey
The Bounty Hunter: Reckoning by Joseph Anderson
Daredevils by Shawn Vestal