i bc27f85be50b71b1 (157 page)
Read i bc27f85be50b71b1 Online
Authors: Unknown








GASTROINTESTINAl SYSTEM 505
Table 8-3. Structure and Function of the Accessory Organs of Digestion
Srructure
Function
Teeth
Break down food {Q combine with saliva.
Tongue
Provides taste sensations by cranial nerve VII (taste).
Keeps the food between the teeth {Q maintain efficient
chewing action for food {Q mix with saliva.
S.lhvary glands
Produce saliva, which is necessary to dissolve food for
tasting and moistens food for swallowing.
Llvcr
Regulates serum levels of fats. proteins, and carbohydrates.
Bile I� produced in the liver and is necessary for the
�lbsorption of lipids and lipid-soluble substances.
The liver also assists with drug metabolism and red blood
cell and vltamm K production.
G..lllhiadder
Stores and releases bile IIltO the duodenum via the hepatic
duct when food enters the stomach.
Pancreas
Exocrme portion secretes bicarbonate and digestive
cl11.ymes into duodenum.
Endocrine portion secretes insulin, glucagons, and
numerous other hormones IO{Q the bloodstream, all of
which are essential in regulating blood glucose levels.
Spleen·
Filters out foreign substances and degenerates blood
cells from the bloodstream.
Also stores lymphocytes.
·Thc '>pleen .\ not part 01 rhe ga�trolllre!lrmal system bur l!i localed ncar or her gasrrolllre�rinal component!. 111 Ihe .lbdonunal caviry.
Source�: Data from JC Scanlon, T Sanders. Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology (2nd
ed). PhLl.1delphta: rA DaVIS, 1993; and AC Guyron, JE Ilall. Texrbook of Medical Phys
Iology (9th cd). Philadelphia: S"unders, 1996;803-844.
History
Before performing the physical examination, the presence or absence
of Items related to GI pathology is ascertained through patient interview, questionnaire completion, or chart review. For a list of these items, see Table 8-4. Appendix I-A also describes the general medical
record review.
Inspection
Figure 8-2 demonstrates the abdominal regions associated with
organ location. DUring inspection, the physical therapist should
notc asymmetries in size and shape in each quadrant, umbilicus


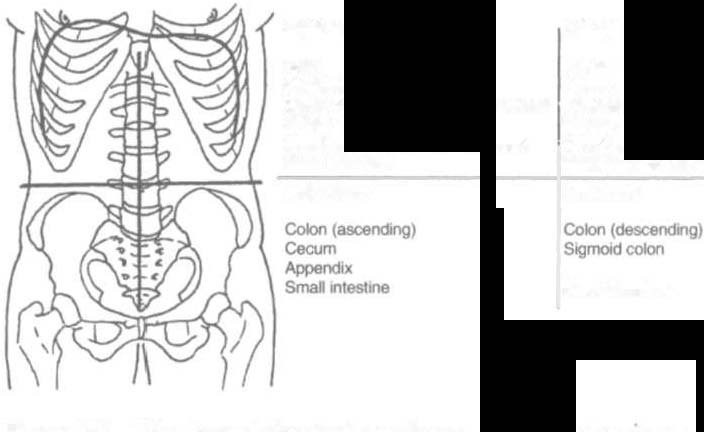

506 AClJfE CARE HANDBOOK FOR PHYSICAL TI-lERAI'ISTS
Table 8-4. Items Associated with Gastrointestinal Pathology
Stool and Urine
Signs and Symptoms
Characteristics
Associated Disorders
Nausea and vomiting
Change In stool color
History of hernia
Hemoptysis
Change in urine color
History of hepatitis
Constipation
Hematochezia (bright
Drug and alcohol
Diarrhea
red blood in srool)
abuse
Jaundice
Melena (black, tarry
Fatty food inrolerance
Heartburn
stools)
Abdominal pain
Sources: Data from MB Koopmeiners. Screening for Gastrointestinal System Disease.
In WG Boisonnauh (cd), Exammation In PhYSical Therapy Practice. New York: