Inverting the Pyramid: The History of Football Tactics (37 page)
Read Inverting the Pyramid: The History of Football Tactics Online
Authors: Jonathan Wilson
Tags: #Non-Fiction, #History

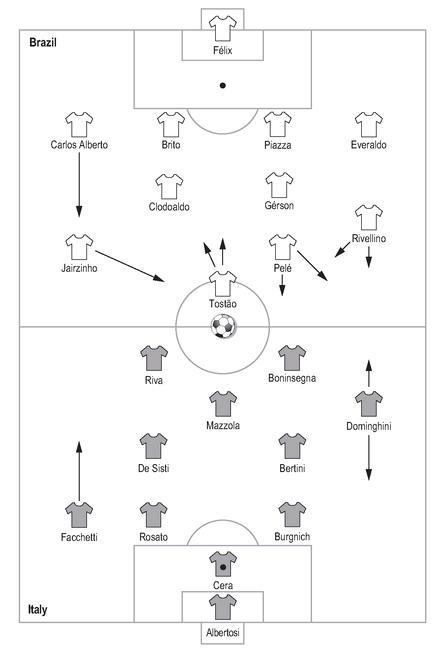
It was not, of course, quite so simple as that, although it is difficult to know just how central Zagallo was. Gérson, Pelé and Carlos Alberto formed a sub-committee of senior players - the
cobras
, as they became known - and it was they who suggested the line-up to Zagallo after a warm-up game against Atlético Mineiro had ended with them being booed off following an uninspiring 3-1 win. The back four was relatively straightforward, with Piazza being used as the
quarto zagueiro
. So, too, was the selection of Gérson, the elegant, deep-lying playmaker - playing as what the Italians would call a
regista
. He needed protection, so Clodoaldo, untouchable after that second Argentina game, operated alongside him, a more physical, defensive presence - he may be best remembered for his part in Brazil’s final goal in the final, dribbling nonchalantly through three Italians in his own half, but that was utterly uncharacteristic.
But what then? Could Pelé and Tostão really play together? ‘Tostão was not a typical centre-forward,’ said the historian Ivan Soter. ‘He was a
ponta da lança
like Pelé. So he would drop off and Pelé would become the centre-forward. It was very fluid.’ The danger then was that there would be nobody in the box to take advantage of their attractive approach play, but that was alleviated by Jairzinho, a rapid right-winger (he more than lived up to his nickname of ‘
Furacão
’ - ‘the Hurricane’) with an eye for goal. His strike against England, hurtling late into the box to hammer an angled finish across Gordon Banks after Pelé had held up and then laid off Tostão’s cross was typical, and he finished the tournament as the only man to score in every game in the finals. In training Gérson spent hours practising clipping diagonal balls for Jairzinho to run onto, in effect calibrating his left foot, making adjustments for the thinness of the Mexican air. Jairzinho’s forward surges left space behind him, but that was no problem because Carlos Alberto was an attacking right-back in the sprit of Nílton Santos. He advanced and the defence shuffled over.
That still left two major issues: who to play on the left, and where to fit Rivellino. He was another who favoured the
ponta da lança
role, and there were question marks over his fitness. Everaldo was a far more defensively-minded full-back, which balanced the back-four, but that meant that if a flying left-winger - like Edu of Santos - were selected, damaging space could appear on that flank, just the sort of weakness Alcide Ghiggia had exploited in the 1950 final. Two problems became one solution, as Rivellino was stationed vaguely on the left, although he often drifted infield, asked to provide some sort of balancing counterweight to Jairzinho’s surges and encouraged to unleash his left foot whenever possible. Was it 4-4-2, was it 4-3-3, was it 4-2-4, was it even 4-5-1? It was all of them and none of them: it was just players on a pitch who complemented each other perfectly. In modern parlance, it would probably have been described as a 4-2-3-1, but such subtleties meant nothing then.
Italy’s coach Ferruccio Valcareggi, meanwhile, dared not play both his great playmakers at the same time, Sandro Mazzola and Gianni Rivera, and so came up with the unhappy compromise of the
staffetta
- the relay - whereby one played the first half, and the other the second. The contrast could hardly have been more pronounced.
Fittingly, Brazil even completed their victory with a goal of supreme quality. No thought from them of sitting on a 3-1 lead, no question of running the clock down. Rather, they simply kept playing, and produced a goal still regularly voted the greatest ever scored, a wonderful parting gift from a wonderful team at a wonderful tournament.
It began with Clodoaldo and his unlikely dribble inside his own half, the thoughtless backheel that, forty-nine minutes earlier, had presented an equaliser to Italy apparently banished from his mind. He fed Jairzinho, now appearing on the left. As Giacinto Facchetti checked his run, the winger turned infield and laid the ball on to Pelé. He waited, and with the same languid precision that had produced goals against England and Uruguay earlier in the competition, he rolled it outside for Carlos Alberto, the full-back and captain, who charged through the space vacated by Jairzinho to flash a first-time shot into the bottom corner.
It was exuberant, it was brilliant and it wasn’t just Brazil that reacted with euphoria, but it marked the end of the age of football’s innocence. In club football, in Europe at least, that era had ended much earlier, but in Mexico, the heat and the altitude combined to make pressing or any kind of systematic closing down of opponents impossible. For the last time in major competition, there was space, and Brazil had a team perfectly equipped to make the best use of it. What had appeared, as satellites beamed it in vibrant technicolour around the world, as the beginning of a brave new world, actually sounded the last post for the old one. And there, perhaps, is the final parallel with the moon landing: the illusory nature of the bold future it seemed to herald. Just as there are no human settlements in outer space, so football has found itself restricted by earthly concerns.
Brazil 4 Italy 1, World Cup Final, Azteca, Mexico City, 21 June 1970
Even Brazil seem to have accepted that 1970 was a zenith never to be repeated. It may have cost him his job, but Saldanha’s assessment of how football was going turned out to have been broadly right - just about twelve months premature. Although the cerebral and aesthetic qualities of the Dutch sides that dominated football in the early seventies were undeniable, they were physically robust and far more conscious of the demands of system than the Brazil of 1970 had been.
The Brazil of 1974 were unrecognisable from that of 1970, something for which Zagallo was widely blamed, although he was not helped by withdrawals. Pelé had retired, while Tostão, Gérson and Clodoaldo were all injured. Still, there was a cynicism to them that had been absent four years earlier, which manifested itself most obviously against Holland in the second group phase. Marinho Peres knocked Johan Neeskens out cold, and Luís Pereira was eventually sent off for a horrible hack on the same player. Holland, who had always had a chip of ice in their hearts, gave as good as they got and won comfortably, 2-0. Brazil finished fourth, but it was widely perceived that that flattered them.
By 1978, Brazil were in the hands of Coutinho, the army captain who had worked with Zagallo in 1970. He insisted his goal was ‘polyvalence’ - which appears to have been another term for Total Football - and as he recalled Francisco Marinho, the adventurous left-back, for the qualifying series, there seemed a measure of truth to that. Come the training camp ahead of the finals, though, and he had fallen back on what he knew best - physical preparation. His side were no more fluent and no less brutal than Zagallo’s team of four years earlier: Coutinho’s relationship with Zico was fractious, Rivellino was unfit and they ended up playing Toninho, a right-back, on the right-wing. Somehow they blundered on to finish third.
Not until 1982 did Brazil really cut loose again, perhaps significantly amid the atrocious heat of Spain. Falcão only started Brazil’s opening game, against the USSR, because Cerezo was suspended, but he played so well he had to be retained, leaving their coach Telê Santana to follow Zagallo’s policy from 1970 and just let his players get on with it. With Zico and Socrates also in the side, Brazil had four vastly talented creative midfielders, but no wide players whatsoever apart from Eder. So again a deficiency was made a virtue as Cerezo and Falcão - both
registas
, deep-lying playmakers - sat behind Zico and Socrates - the
trequartistas
- while Eder was deployed as an auxiliary centre-forward, playing off the lumbering Serginho, who would surely never have been anywhere near the side had either Reinaldo or Careca been fit.
The formation was thus a 4-2-2-2, with a strong central column flanked by two marauding full-backs in Leandro and Júnior. In a European context, it would have been perceived as lacking width, but this was a team of such fluency and poise in possession that they created it with their movement. It was a system that never spread - the Brazilian coach Vanderlei Luxembourgo’s attempts to institute what he called ‘the magic quadrilateral’ at Real Madrid in 2005 failed amid general bewilderment - but it seemed to suit the Brazilian mentality, the two deep-lying midfielders (by 1994, when Dunga and Mauro Silva occupied the positions, they would be
bona fide
holding players) providing a platform for four out-and-out attacking players - two centre-forwards and two
trequartistas
- while still allowing the full-backs to tear up and down the flanks as they had been doing in Brazil since the days of Nílton Santos.
The Brazil of 1982 produced the most exhilarating football the World Cup had known since 1970. They beat the USSR 2-1, swatted aside Scotland 4-1 and New Zealand 4-0, playing an effortless, fluid game full of deliciously angled passes and fearsome long-range shooting. In the second group phase, they comfortably beat the reigning world champions Argentina, leaving them needing just a draw against Italy to reach the semi-finals. It was considered a formality.
Italy were in the phase of
il gioco all’ Italiana
rather than out-and-out
catenaccio
, but they were still notably defensive. Just as much as the game in the Azteca in 1970, their meeting with Brazil in the Estadi de Sarrià was seen as an allegory. To try to alleviate the shortfall in midfield caused by Herrera’s version of
catenaccio
, Italian football had followed the route of Dutch and German football, by making the
libero
a far more rounded player - a converted inside-forward such as Pierluigi Cera or Gaetano Scirea rather than a converted full-back like Ivano Blason or Armando Picchi - capable of stepping out from the back and making an extra midfielder when his side had possession.
Italy had begun the tournament slowly, progressing through the first group - in which they drew all three of their games - only by virtue of having scored a goal more than Cameroon, who also drew all three of their matches. Paolo Rossi, returning after a ban for his involvement in a match-fixing scandal, looked far from his best, but a 2-1 win over Argentina gave them belief, and raised doubts among the Brazilians. Waldir Peres, the latest in a long line of hapless Brazilian goalkeepers, admitted before the game that his great fear was that Rossi would suddenly spring into life. He proved a far better mystic than he was goalkeeper.
Was it the greatest World Cup game ever? Probably, although Hungary’s 1954 victory over Uruguay will always have its devotees. Certainly it had an epic feel, something enhanced by overcrowding as far more than the official 44,000 squeezed in. Had Brazil scored an early goal, Italy could easily have wilted, their system and their mentality not equipped for chasing a game, but it was the Italians who took a fifth-minute lead, as Bruno Conti, having been allowed to advance almost forty yards down the right, cut infield and released the attacking left-back Antonio Cabrini, who crossed for Rossi to repay the faith of his manager Enzo Bearzot with a fine header.
And so was set in motion the pattern for the game: Brazilian attacking, and Italian resistance. Within seven minutes, it was level, as Socrates played a one-two with Zico, and advanced to drive the ball in at Dino Zoff’s near post. Then surely, it seemed, Brazil would kick on to win. Perhaps they would have done, had it not been for a dreadful error from Cerezo after twenty-five minutes, casually knocking a square pass in the vague direction of Júnior. Rossi, suddenly a poacher again, stole in, and beat Waldir. This time the lead lasted, and Brazil became increasingly edgy. Rossi, with the chance to make it 3-1 midway through the second half, sidefooted badly wide, and when, two minutes later, Brazil equalised through Falcão’s ferocious drive, it looked once again as though they would prevail.
Perhaps, needing only a draw to progress, they should have tightened up and held what they had, but that was not the Brazilian way. They kept attacking, and paid the price. A Conti corner was half-cleared, Marco Tardelli half-hit his shot from the edge of the box and Rossi, played onside by a dozing Júnior, hooked the ball past Waldir. It was, as Glanville said, ‘the game in which Brazil’s glorious midfield, put finally to the test, could not make up for the deficiencies behind and in front of it.’
It was a game, moreover, that lay on a fault-line of history and, unlike 1970, football followed the victors, in style if not in formation. Zico called it ‘the day that football died’, but that is to percolate everything through the consciousness of a particularly romantic Brazilian. Rather it was the day that a certain naivety in football died; it was the day after which it was no longer possible simply to pick the best players and allow them to get on with it; it was the day that system won. There was still a place for great individual attacking talents, but they had to be incorporated into something knowing, had to be protected and covered for.