Secondary Schizophrenia (116 page)
Read Secondary Schizophrenia Online
Authors: Perminder S. Sachdev

Linkage regions (asterisks indicate significant genomewide evidence):
1p36-p35 [120], [121]
1p21-p13 [122]
∗
1q21-q24: [123]
∗
, [124]
1q32-q42: [125]
∗
, [115], [126]
∗
, [127]
2p15-p13: [128]
∗
, [129], [130]
2p12-q14: [113], [131]
5q22-q35: [120], [127], [128], [130], [132], [133], [134], [135]
6p24-p22: [135], [136], [137], [138], [139], [140]
6q21-q25: [141], [142], [143]
∗
, [109], [144]
∗
8p23-p21: [145]
∗
, [123], [127], [135], [146], [147]
10p15-p12: [132]
∗
, [139], [148], [149]
10q22-q26: [137]
∗
, [143], [150], [151]
∗
, [152]
13q31-q34: [121], [145]
∗
, [153]
15q13-q14: P50 inhibitory deficit [154]
∗
; Periodic catatonia [155]
∗
, [137], [141], [156], [157]
17p11-q25: [151], [158]
∗
22q11-q12: [132], [145], [151], [155], [158], [159]
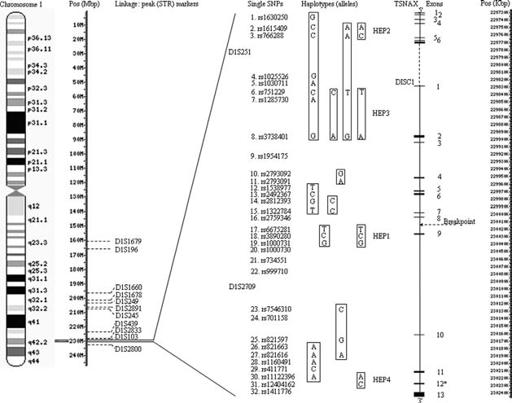
Chromosome ideograms were adapted from Ensembl Genome Browser (August, 2006).
of genomic DNA, comprises a 13-exon transcript of
combined Finnish sample was observed for a marker
∼
7.5 Kb, and encodes a novel protein of 854 AAs)
located within DISC1, D1S2709. A follow-up study of
[192].
DISC2 specifies an antisense noncoding RNA
70 Finnish families
[201]
observed maximal linkage
molecule believed to be involved in regulating DISC1
(LOD
=
2.70) with an intragenic SNP, rs1000731.
expression
[193].
Other populations have reported linkage of the
Multiple independent observations of a rearrange-
DISC1 region to SZ
[200],
Schizoaffective Disorder
ment affecting a particular gene would be strong evi-
(SA)
[203],
and Bipolar Disorder (BP)
[198, 199, 215,
dence for the involvement of this gene in the patho-
216],
and associations for SZ, BP, SA, and Major
physiology of SZ
[214]
. This evidence is currently
Depressive Disorder
[205, 208, 210, 211].
lacking. However, the original linkage finding has
Since the initial linkage reports, numerous stud-
been extended to the general Scottish population
[205,
ies have shown association of DISC1 variants with SZ
208]
and beyond. Linkage of this region of 1q to SZ
(Figure 23.2).
Although some consistency has been
has also been detected in an internal Finnish isolate
observed across studies, the associated haplotypes
[122]
and families from across Finland
[125].
The
vary widely in their location within DISC1 and their
strongest evidence for linkage (LOD
=
3.21) in the
constituent alleles. In a study conducted in 458 Finnish
Organic Syndromes of Schizophrenia – Section 3
Table 23.1
Schizophrenia candidate genes and strength of evidence
Strength of evidence (0 to 5)
References:
Linkage
Altered
original
to gene
Association
Biological
report(s) /
Gene
Location
locus
with SZ
Cytogenetics
plausibility
review(s)
DTNBP1
6p22
+ + ++
+ + + + +
++
Yes,
++
[171] / [172]
NRG1
8p12-21
+ + ++
+ + + + +
+ + +
Yes,
+
[173] / [174]
DISC1
1q42
++
+ + ++
+ + + + +
+ + ++
Yes,
+
[115], [175] / [176]
RGS4
1q21-22
+ + +
+ + +
++
Yes,
++
[177], [178] / [159],
[179], [180]
COMT
22q11
+ + ++
+
+ + + + +
+ + ++
Yes,
+
[181] / [118], [119]
DAOA
13q32-34
++
+ + +
++
Not known
[182] /[183], [184]
(G72/G30)
PPP3CC
8p21
+ + ++
+
+ + ++
Yes,
+
[185], [186] / [168]
CHRNA7
15q13-14
+
++
+ + +
Yes,
+ + +
[154], [155] / [49]
AKT1
14q22-32
++
+
++
Yes,
++
[164] / [187]
DRD3
3q13
++
+ + +
Yes,
++
[188] / [160], [161]
5HT2A
13q14.2
++
+ + +
Yes,
++
[189] / [162], [163]
Notes. Adapted from [167]; DTNBP1: dystrobrevin binding protein 1; NRG1: neuregulin 1; DISC1, disrupted in schizophrenia 1; RGS4, regulator of G-protein signaling 4; COMT, catechol-O-methyltransferase; DAOA, D-amino acid oxidase activator; PPP3CC, protein phosphatase 3
(formerly 2B), catalytic subunit, gamma isoform (calcineurin A gamma); CHRNA7, cholinergic receptor, nicotinic, alpha 7; AKT1, v-akt murine
thymoma viral oncogene homolog 1; DRD3, dopamine receptor D3; 5HT2A, 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 2A.
SZ pedigrees, Hennah and colleagues
[204]
identified
ation of HEP1 (SNPs 17–19) has been reported by two
four DISC1 haplotypes (termed HEP 1 to 4) associ-
Finnish studies, for SZ p
=
0.0009
[201]
and seman-ated with a broad diagnostic model (SZ/SA/BP/MDD).
tic clustering (p
=
0.006)
[206].
A second cytogenetic
Association of the HEP3 haplotype was only signifi-abnormality has also been reported within exon12 (a
cant for affected females (p
=
0.00024) but showed a
four base-pair deletion at the 3’ end of DISC1) in three
trend with negative symptoms and hallucinations in
affected siblings and their unaffected father
[194],
both sexes. Other studies have reported association
although involvement of this deletion with SZ has
with the HEP3 haplotype
[208]
and larger haplotypes
not yet been statistically supported. Negative reports
containing HEP3
[205, 206]
, although the associated
include a large Japanese sample
[217].
haplotypes differ in their component alleles (Figure
23.2). These larger haplotypes also involve variants
within the adjacent translin-associated factor X gene
Endophenotypes
(TSNAX). Additionally, the largest associated haplo-Initially, Blackwood
[115]
reported amplitude reduc-type (SNPs 1–8) demonstrated association with BP
tion and latency prolongation in the auditory P300
in females (p
=
0.00026)
[205].
Using 102 Taiwanese
event-related potential in translocation carriers and
affected sib-pair families, Liu and colleagues
[209]
those with SZ compared with noncarriers and con-
screened 12 genes within 1.5 megabases of D1S251
trols. Apart from a recent SZ dimensional study of
(within DISC1) to fine-map their chromosome 1 link-lifetime severity of delusions
[213]
, other endopheno-age peak
[200].
Two haplotypes showed association
typic reports include impairments in spatial working
with a subgroup of SZ with sustained attention deficits;
memory
[197,
206, 211, 218]
, short-term visual work-one was in DISC1, 3 of HEP3 (SNPs 10, 11: p
=
ing memory and visual attention
[207],
verbal working
0.0008), the other was located within glyceronephos-memory
[218],
sustained attention deficits
[209],
and
phate O-acyltransferase (GNPAT)
[209].
Even further
semantic processing in long-term memory
[206].
Neu-
3 of HEP3, near the translocation breakpoint, associ-roimaging variables showing association with DISC1
Chapter 23 – The status of genetic investigations of schizophrenia
Figure 23.2
Genomic position, structure and published findings on DISC1 (and TSNAX)
Notes. Chromosome 1 ideogram, positions (Mbp
=
megabases; Kbp
=
kilobases), TSNAX
=
translin-associated factor X gene;
DISC1
=
Disrupted in Schizophrenia 1; STR markers
=
simple tandem repeat markers; SNP
=
single nucleotide polymorphism; SNPs 1–31 are
taken from the DISC1 literature; Haplotypes
=
linear arrangement of closely linked alleles inherited as a unit on one member of a
chromosome pair; global p values incorporate multiple test correction; unless otherwise indicated, all scores are for the schizophrenia (SZ)
phenotype; BP
=
Bipolar Disorder; SA
=
Schizoaffective Disorder; MDD
=
Major Depressive Disorder;
Translocation breakpoint: LOD
=
7.1 (SZ, BP, MDD)
[115]
Exon 12
∗
: Frameshift site(s) identified in single U.S. multiplex SZ pedigree
[194]
Linkage STR markers:
D1S1679: LOD
=
6.50 [123]
D1S196: LOD
=
3.20 [127]; LOD
=
2.40 [124]
D1S249: LOD
=
2.00 [195]
D1S2891: LOD
=
3.82 [125]; LOD
=
2.67 [195]
D1S245: LOD
=
3.46 [126]
D1S439: LOD
=
2.62 [196]
D1S2833: p
=
0.007 spatial working memory deficit in SZ [197]
D1S103: LOD
=
2.63 BP [198]; LOD
=
2.39 BP, SA, MDD [199]
D1S251(intragenic): LOD
=
2.18 [200]
SNP 19 (rs1000731)(intragenic): LOD
=
2.70 [201]
D1S2709 (intragenic): LOD
=
3.21 [126]; 3.31 [202]
D1S2800: LOD
=
3.54 [203] SA
SNP markers/haplotypes:
HEP1 (SNPs 17–19), HEP2 (SNPs 2, 3), HEP3 (SNPs 6, 8), HEP4 (SNPs 30, 31): haplotypes identified by Hennah et al., 2003 [204]
SNPs 1–8 (global p
=
0.0066: BP); SNPs 14–15 (C-C): (global p
=
0.0044: SZ); SNPs 12–15 (global p
=
0.00026: BP females; (global p
=
0.0016): BP
males & females, 26–30 (global p
=
0.0053) [205]
SNPs 2, 3, 6, 8 (A-A-T-G): p
=
0.001; choice reaction time p
=
0.002 [206]
SNPs 6, 8 (Arg264Gln) (T-A): males and females: (global p
=
0.0031); affected females: (global p
=
0.00024) [204]; short-term visual working
memory (p
=
0.0013) and visual attention (p
=
0.0079) deficits [207]
SNPs 6, 8 (C-A): p
=
2.4
×
10
−
22 [208]
SNP 10: p
=
0.0053; SNPs 10, 11 (G-A): p
=
0.0008 SZ with sustained attention deficit [209]
SNP 17 (Leu607Pro): p
=
0.2.3
×
10
−
6 [210]
SNPs 17–19: p
=
0.0009 [201]; p
=
0.02 [206]; p
=
0.006 semantic clustering [206]
SNPs 23, 25, 27 (C-G-A) (Global p
=
0.002); SNP 25 (A) (p
=
0.004) [211]
SNP 27 (ser704cys)(G) (p
=
0.005) MDD [212]; (p
=
0.002) lifetime severity of delusions in SZ [213]