Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis (1078 page)
Authors: Mary A. Williamson Mt(ascp) Phd,L. Michael Snyder Md

BOOK: Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis
3.93Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
One of the more common causes of a false-positive result is unusually rapid clearance of metyrapone from the plasma, resulting in inadequate blockade of cortisol biosynthesis. This is manifested by a serum cortisol concentration >7.5 μg/dL in the sample drawn at 8
AM
in the overnight test, by a serum cortisol concentration >5 μg/dL 4 hours after the last dose of metyrapone, or by urinary cortisol excretion >20 μg/24 hours the day metyrapone was administered in the standard 2-day test.
MICROALBUMIN, URINE
Definition
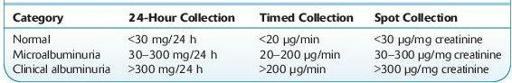
The urine dipstick is a relatively insensitive marker for proteinuria, not becoming positive until protein excretion exceeds 300–500 mg/day. The normal rate of albumin excretion is <20 mg/day (15 μg/minute); persistent albumin excretion between 30 and 300 mg/day (20 and 200 μg/minute) is called microalbuminuria. Albumin excretion >300 mg/day (200 μg/minute) is considered to represent overt or dipstick positive proteinuria (also called macroalbuminuria).
In type 1 and 2 DM, the presence of microalbuminuria on repeat specimens collected in the basal state may signify early diabetic nephropathy. It is a marker, in patients with or without diabetes, for cardiovascular mortality. For a definition of microalbuminuria, see Table 16.56.
Measurement of the urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio in an untimed urinary sample is the preferred screening strategy for microalbuminuria. This test has several advantages: it does not require early morning or timed collections, it gives a quantitative result that correlates with the 24-hour urine values over a wide range of protein excretion, it is simple to perform and inexpensive, and repeat values can be easily obtained to ascertain that microalbuminuria, if present, is persistent.
Other name: albumin/creatinine ratio.

Normal range:
Albumin/creatinine ratio (random urine): <30.0 μg/mg creatinine
Microalbumin excretion (24-hour urine): 0–29.9 mg/day
TABLE 16–56. American Diabetes Association Definition of Microalbuminuria
Use
Diagnosis of kidney dysfunction.
Other books
Zoe Thanatos by Crystal Cierlak
The Wicked Game (A Wicked Game Novel) by Fuller, Olivia
The Executor by Jesse Kellerman
The Professor's Pet (A BDSM Romance Novel) by Crescent, Tara
The Runaway by Grace Thompson
Blood Warrior (The Arcadia Falls Chronicles #4) by Malone Wright, Jennifer
Ask For It by Selena Blake
The Society by Michael Palmer
A Marriage In Wyoming (The Marshall Brothers 3) by Lynnette Kent
The Lady of Bolton Hill by Elizabeth Camden