Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis (1429 page)
Authors: Mary A. Williamson Mt(ascp) Phd,L. Michael Snyder Md

BOOK: Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis
13.81Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
Nontraditional testing algorithm: When reverse sequence screening (Figure
17-2
) is used, all appropriate reflexing criteria should be used. FTA-ABS test should not be used to confirm discordant treponemal screening results.
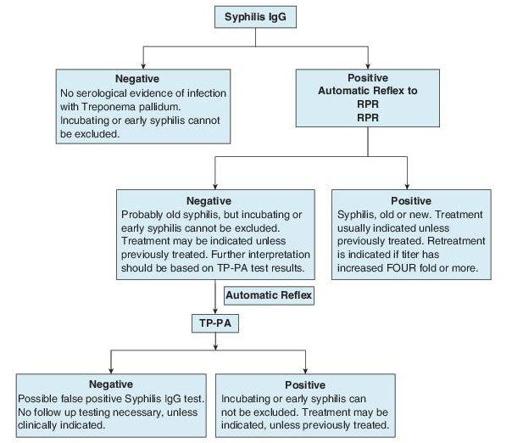
Figure 17–2
Nontraditional algorithm for syphilis testing. RPR, rapid plasma reagin (test); TP-PA, Treponema pallidum particle agglutination (test).
Suggested Reading
Discordant results of reverse sequence syphilis screening-Five laboratories; United States 2006– 2010.
MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep.
2011;60:133.
THROAT CULTURE (ROUTINE)
Definition and Use
This culture is primarily used to detect group A beta-hemolytic
Streptococcus
(GABHS,
S
.
pyogenes
) from throat swabs. This test is used, usually in children, who present with symptoms of streptococcal pharyngitis. Patients typically present with moderate to severe pharyngitis along with systemic symptoms, including fever, malaise, headache, and abdominal pain. Runny nose, cough, diarrhea, and other symptoms are more suggestive of another cause, usually viral.
A GABHS throat culture is recommended to confirm negative
S
.
pyogenes
antigen screening tests in children. Confirmatory cultures are not needed for adults with negative antigen test results if the sensitivity of the specific antigen test used is >80%.
The importance of diagnosis of GABHS pharyngitis is for the prevention of nonsuppurative sequelae. Antibiotic treatment given during the acute phase of GABHS infection is effective in prevention of RF, glomerulonephritis, and other complications. GABHS pharyngitis may also be complicated by peritonsillar abscess or other suppurative pararespiratory infections.
A GABHS throat culture is not recommended for test of cure after therapy for documented strep throat; cultures may demonstrate clinically insignificant low-level carriage after successful therapy.

Special collection and transport instructions:
Affected tonsillar and posterior pharyngeal mucosa is rubbed vigorously with a swab, carefully avoiding contamination by the tongue, buccal, or other mucosal surface.
The swab is transported to the laboratory in transport media according to routine recommendations for bacterial specimens.
Throat swabs are inoculated onto SBA; selective agar is inoculated by some laboratories to suppress the growth of normal endogenous flora and to facilitate isolation of GABHS. Cultures are incubated for 24–48 hours.

S
.
pyogenes
isolates remain predictably susceptible to penicillin, the treatment of choice. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing is not performed unless requested because of penicillin allergy.
Other books
Black Widow by Jessie Keane
The Rebellious Twin by Shirley Kennedy
Cocaine Wars by Mick McCaffrey
Dark Enchantment by Janine Ashbless
Siege of Macindaw by John Flanagan
Fangtastic by Lucienne Diver
Origins (Remote) by Drouant, Eric
A Crazy Day with Cobras by Mary Pope Osborne
Handfasted (To Love a Governess Novella) by Jane Charles
Creola's Moonbeam by McGraw Propst, Milam