Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis (935 page)
Authors: Mary A. Williamson Mt(ascp) Phd,L. Michael Snyder Md

BOOK: Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis
4.45Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
Sideroblastic anemia
Pregnancy
Whipple disease
Amyloidosis
Limitations
Serum folate is a relatively nonspecific test. Low serum folate levels may be seen in the absence of deficiency, and normal levels may be seen in patients with macrocytic anemia, dementia, neuropsychiatric disorders, and pregnancy disorders.
Patients with low RBC folate or megaloblastic anemia should be evaluated for vitamin B
12
deficiency. To distinguish between vitamin B
12
and folate deficiency, determination of homocysteine (HCS) and methylmalonic acid (MMA) will help. In vitamin B
12
deficiency, both HCS and MMA are elevated, whereas in folate deficiency, only HCS levels are elevated.
FOLLICULAR-STIMULATING HORMONE (FSH) AND LUTEINIZING HORMONE (LH), SERUM
Definition
These glycoproteins are produced by the anterior pituitary gland, regulated by hypothalamic gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) and feedback by gonadal steroid hormones. FSH stimulates follicular growth and stimulates seminiferous tubules and testicular growth. LH stimulates ovulation and production of estrogen and progesterone. LH controls production of testosterone by Leydig cells.

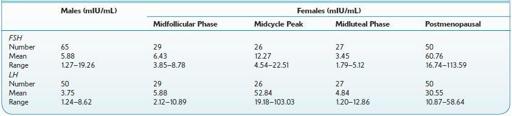
Normal range:
see Table 16.34.
TABLE 16–34. Normal Ranges of Human FSH and LH
Use
Diagnosis of gonadal, pituitary, hypothalamic disorders
Other books
Thanksgiving on Thursday by Mary Pope Osborne
Tantric Orgasm for Women by Diana Richardson
The Serenity Murders by Mehmet Murat Somer
Jailbait by Jack Kilborn
Crisis Four by Andy McNab
Love Notes (Rocked by Love #1) by Susan Scott Shelley
The Good Doctor's Tales Folio Four by Randall Farmer
Fearless by O'Guinn, Chris
Eat My Heart Out by Zoe Pilger