How to Think Like Sherlock (3 page)
Read How to Think Like Sherlock Online
Authors: Daniel Smith


Quiz 2 – Number Sequences
Have a look at the following sequences of numbers. Complete the sequence in each case.
1. 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, ___
2. 3, 9, 27, 81, 243, ___
3. 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, ___
4. 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, ___
5. 12, 33, 14, 30, 16, 27, 18, 24, 20, 21, ___
6. 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, ___
7. 42339, 648, 192, 18, ___
Quiz 3 – Word Ladders
Here are a couple of word ladders. Starting with the word at the top of each ladder, can you change a single letter at a time to create a new word on each rung and arrive at the word at the foot of the ladder?
i) Cat
_____
_____
_____
_____
Kid
ii) Game
_____
_____
_____
_____
_____
Foot
Quiz 4 – Word Wheel
To finish off your initial mental stretches, here is a word wheel. Copy it quickly onto a separate piece of paper. Each answer begins at the outside of the wheel and ends with the ‘T’ at the centre. When you have finished, the letters around the edge of the wheel should spell a familiar name.
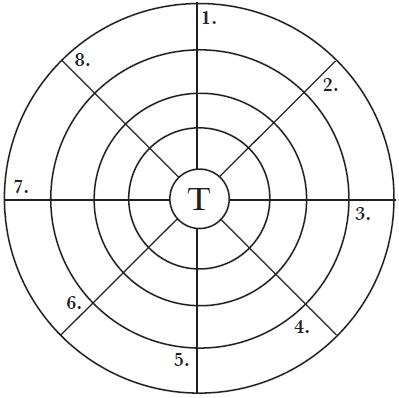
1. A first version.
2. Sunday lunch?
3. A popular card game.
4. Head of a monastery.
5. A characteristic.
6. Animal once prized for its fur.
7. Not discreet.
8. As dark as ...
Being Alert to the World Around You
‘You see, but you do not observe. The distinction is clear.’
‘A SCANDAL IN BOHEMIA’
Holmes’s powers of observation were unmatched. He could scan a scene and alight on a telling detail that countless others had missed. He stated as much in ‘The Boscombe Valley Mystery’: ‘You know my method. It is founded upon the observation of trifles.’
Some of us are born more observant than others but it is nonetheless an ability that can be developed by hard work and dedication. Seeing – that is, perceiving with the eyes – is easy; observation – absorbing into your brain the data provided by your eyes – is much more taxing. Could you say what your nearest-and-dearest was wearing the last time you saw them, or what the colour of the last car that passed you was? What is the registration number of your next-door neighbour’s car? As Holmes remarked in
The Hound of the Baskervilles
, ‘The world is full of obvious things which nobody by any chance ever observes.’
If it is not a skill that comes easily to you, try consciously ‘observing’ in your daily life. If you’re on a bus or sitting in a café, look at those around you (while trying not to appear like a crazed, staring stalker!). The more you practise the skill, the more natural it will become. Holmes was the undisputed master of this particular talent. Consider ‘The Adventure of the Second Stain’, in which our intrepid hero spots the lack of correlation between a bloodstain on a carpet and the floorboards beneath. It was this spot, missed by a troop of investigating policemen, that paved the way to the case’s ultimate conclusion. Similarly, in ‘The Disappearance of Lady Frances Carfax’, Holmes makes a crucial observation about the depth of a coffin, though in the process rues the fact that he had not made his observation earlier: ‘It had all been so clear, if only my own sight had not been dimmed.’

Keeping an Ear to the Ground
‘My night was haunted by the thought that somewhere a clue, a strange sentence, a curious observation, had come under my notice and had been too easily dismissed.’
‘THE DISAPPEARANCE OF LADY FRANCES CARFAX’

Just as important as developing your visual observation skills is improving your listening abilities. After Holmes had made the observation above in the case of Lady Carfax, he revealed that ‘in the gray of the morning, the words came back to me’, recalling an apparently off-the-cuff utterance from the previous day that would serve to help him resolve the case. In another story, ‘The Adventure of the Speckled Band’, he understands the importance of a ‘low, clear whistle’ in the dead of night better than any other figure in the story, with the exception of the perpetrator of a terrible crime. In the same way that Holmes could attach meaning to what his eyes saw like few others, he could grasp the connotations of sound quite magnificently (even when that sound was relayed to him by a witness rather than heard by his own ears).
One of the most famous observations in the whole of the Holmes canon reminds us that when we listen, it may be something that we don’t hear that proves just as important as something we do hear. The observation is that concerning ‘the curious incident of the dog in the night-time’, namely the dog that didn’t bark in ‘Silver Blaze’. For most of us, the silence of a dog would be suggestive of very little but when this detail was discerned by the Great Detective, he was able to read much into it:
I had grasped the significance of the silence of the dog, for one true inference invariably suggests others. The Simpson incident had shown me that a dog was kept in the stables, and yet, though someone had been in and had fetched out a horse, he had not barked enough to arouse the two lads in the loft. Obviously the midnight visitor was someone whom the dog knew well.
As with improving your visual observation, the key to listening better is to consciously practise. We listen in two ways: passively – when we listen to the radio, sit in a lecture or are walking down the street – and actively – for example, when we are participating in a dialogue.
There are a few simple exercises you can use to become a better listener. Tune in to the hourly news bulletin on the radio. Really focus in on what is being related. When the broadcast finishes, switch off the radio and jot down some notes about what was said. Can you remember each of the stories in the right order? And can you recall the broad subject or have you retained some serious detail from each? When you begin, you might be rather shocked by how little has soaked in. But if you keep up the practice for a while, you will likely see some striking improvement. Similarly, sit in your garden on a summer’s afternoon. Close your eyes but keep your ears open. Note all the different sounds that you can hear, whether man-made or from nature. Such an exercise can help you become better attuned to the environment around you.
Improving your listening skills when you are part of a dialogue is a different challenge altogether. For the majority of us, when we converse we are more interested in being heard than hearing. But by being this way, we risk missing out on learning lots of new information that might prove very valuable to us. Here are a few tips for improving your listening skills when in conversation:
Ask questions
That way, you encourage the other person to speak and yourself to listen.
Don’t interrupt
Avoid the temptation to interrupt, even if it is to agree with the other person. Listening and speaking at the same time is a very difficult skill to master.
Focus on the speaker
It sounds so obvious but think how often you have been introduced to someone only to forget their name a moment later.

