HTML The Definitive Guide (56 page)
Read HTML The Definitive Guide Online
Authors: Chuck Musciano Bill Kennedy

5.3 Document Colors and
Background Images



5.3 Document Colors and Background Images
The HTML 4.0 standard provides a number of attributes for the
author to define text, link, and document background colors, in addition to defining an image to be used as the document background. Internet Explorer extends these attributes to include document margins and better background image control. And, of course, the latest style sheet technologies integrated into the current browsers let you manipulate all these various display parameters.
5.3.1 Additions and Extensions to the Tag
The attributes that control the document background, text color, and document margins are used with the
[, 3.7]
5.3.1.1 The bgcolor attribute
One standard way you can change the default background color in the browser window to another hue with the bgcolor attribute for the
tag. Like the color attribute for the tag, the required value of the bgcolor attribute may be expressed in either of two ways: as the red, green, and blue (RGB) components of the desired color or as a standard color name.Appendix F, provides a
complete discussion of RGB color encoding along with a table of acceptable color names you can use with the bgcolor attribute.
Setting the background color is easy. To get a pure red background using RGB encoding, try:
For a more subtle background, try:
5.3.1.2 The background attribute
If a splash of color isn't enough, you may also place an image into the background of a document with the background attribute in its
tag.The required value of the background attribute is the URL of an image. The browser automatically repeats (tiles) the image both horizontally and vertically to fill the entire window.
You normally should choose a small, somewhat dim image to create an interesting but unobtrusive background pattern. Besides, a small, simple image traverses the network much faster than an intricate,
full-screen image.
Figure 5.20 shows you how the extended browsers repeatedly render a single brick to create a wall of
bricks for the document background:
Figure 5.20: One brick becomes many in a Netscape background
Background images of various dimensions and sizes create interesting vertical and horizontal effects on the page. For instance, a tall skinny image might set off your document heading: Kumquat Lore
For centuries, many myths and legends have arisen around the kumquat.
If the
vertical_fountain.gif
is a narrow, tall image whose color grows lighter towards its base and whose length exceeds the length of the document body, the resulting document might look like the one shown in
Figure 5.21
.
Figure 5.21: A tall and skinny background

You can achieve a similar effect horizontally with an image that is much wider than it is long (see
Figure 5.22).
Figure 5.22: A long and skinny background
The background attribute is deprecated in HTML 4.0, since you can achieve similar effects using style sheets.
5.3.1.3 The bgproperties attribute
The bgproperties attribute extension for the
tag is exclusive to Internet Explorer and works only in conjunction with the background attribute extension. The bgproperties attribute has a single value, fixed. It freezes the background image to the browser window, so it does not scroll with the other window contents. Hence, the exampleH2Omark.gif
background image servers as a watermark for the document:
5.3.1.4 The text attribute
Once you alter a document's background color or add a background image, you also might need to adjust the text color to ensure that users can read the text. The HTML 4.0 text standard attribute for the
tag does just that: it sets the color of all nonanchor text in the entire document.Give the text attribute a color value in the same format as you use to specify a background color (see bgcolor
in section 6.3.1.1) - an RGB triplet or color name, as described in Appendix F
. For example, to produce a document with blue text on a pale yellow background, use:
The text attribute is deprecated in HTML 4.0, since you can achieve similar effects using style sheets.
5.3.1.5 The link, vlink, and alink attributes
The link, vlink, and alink attributes of the
The link attribute determines the color of all hyperlinks the user has not yet followed. The vlink attribute sets the color of all links the extended browser user had followed at one time or another. The alink attribute defines a color for active link text - one that is currently selected by the user and is under the mouse cursor with the mouse button depressed.
Like text color, you should be careful to select link colors that can be read against the document background. Moreover, the link colors should be different from the regular text as well as from each other.
These attributes are deprecated in HTML 4.0, since you can achieve similar effects using style sheets.
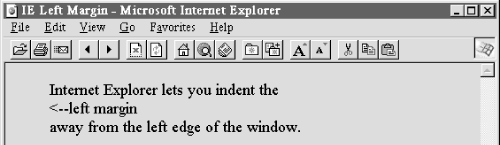
5.3.1.6 The leftmargin attribute
Peculiar to Internet Explorer, the leftmargin attribute extension for the
tag lets you indent the left margin relative to the left edge of the browser's window, much like a margin on a sheet of paper. Other browsers ignore this attribute and normally left-justified body content abuts the left edge of the document window.The value of the leftmargin attribute is the integer number of pixels for that leftmargin indent; a value of 0 is the default. The margin is filled with the background color or image.
For example, Internet Explorer renders the following text justified against a margin 50 pixels away from the left edge of the browser window (see
Figure 5.23):
Internet Explorer lets you indent the
<--left margin