Muslim Fortresses in the Levant: Between Crusaders and Mongols (169 page)
Read Muslim Fortresses in the Levant: Between Crusaders and Mongols Online
Authors: Kate Raphael
Tags: #Arts & Photography, #Architecture, #Buildings, #History, #Middle East, #Egypt, #Politics & Social Sciences, #Social Sciences, #Human Geography, #Building Types & Styles, #World, #Medieval, #Humanities

Rossabi, M.,
Khubilai Khan
(Berkeley, Los Angeles and London, 1988).
Runciman, S.,
A History of the Crusades
(London, 1994), vol. 3.
al-Sarraf, S., “Mamluk Furūsīya literature and its antecedents,”
MSR
8/1 (2004): 141–200.
Sauvaget, J., “ ,”
,”
EI
2
3 (1979): 85–90.
Schein, S.,
Fideles Crucis: The Papacy, the West and the Recovery of the Holy Land 1274–1314
(Oxford, 1991).
Sen-Dou Chang, “The morphology of walled capitals” in
The City in Late Imperial China
, ed. G. W. Skinner (Stanford, 1977), 75–100.
Serjeant, R. B.,
The Portuguese off the South Arabian Coast: Hadrami Chronicles
(Beirut, 1974).
Shapira, Y., “The tower in the Crusader Kingdom of Jerusalem,” MA thesis, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem (2000). [Hebrew]
Sharon, M.,
Corpus Inscriptionum Arabicarum Palaestinae
(Leiden, Boston and Cologne, 1999), vol. 2.
Silverstein, A. J.,
Postal Systems in the Pre-Modern Islamic World
(Cambridge, 2007).
Sinclair, T. A.,
Eastern Turkey: An Architectural and Archaeological Survey
, 4 vols (London, 1990).
Sinor, D., “On Mongol strategy,”
Inner Asia and its Contacts with Medieval Europe
(London, Variorum, 1977), XVI, 238–49.
Smail
,
R C.,
Crusading Warfare (1097–1193)
(Cambridge, 1956).
——
Crusading Warfare (1097–1193)
, 2nd edn (Cambridge, 1995).
Smith, J. M. Jr. “Mongol manpower and Persian population,”
JESHO
18 (1975): 271–99.
——“Ayn Jālūt: Mamluk success or Mongol failure?,”
HJAS
44 (1984): 307–45.
——“Demographic considerations in Mongol siege warfare,”
Archivum Ottomanicum
13 (1993–4): 229–334.
——“Mongol society and military in the Middle East: antecedents and adaptations,” in
War and Society in the Eastern Mediterranean 7th–15th Centuries
, ed. Y. Lev (Leiden, NY, and Cologne, 1997), 249–66.
Sobernheim, M., “Die arabischen Inschriften von Aleppo,”
DI
15 (1926): 162–210.
Somogyi, J., “Adh-Dhahabi’s record of destruction of Damascus by the Mongols in 699–700/1299–1301,” in
Ignace Goldziher Memorial Volume
, eds S. Lowinger and J. Somogyi (Budapest, 1948), 353–86.
Sourdel, D., “Barīd,”
EI
2
1 (1960): 1045–6.
——“Karak,”
EI
2
4 (1978): 609.
——“Ibn Shaddād,”
EI
2
3 (1979): 933.
Stark, F.,
Rome on the Euphrates
(London, 1966).
Stewart, A. D.,
The Armenian Kingdom and the Mamluks: War and Diplomacy during the Reign of II (1289–1307
II (1289–1307
), The Medieval Mediterranean, vol. 37 (Leiden, 2001).
——“ al-Rūm/Hrmogla/Rumkale and the Mamluk siege of 691 ah/1291ce,” in
al-Rūm/Hrmogla/Rumkale and the Mamluk siege of 691 ah/1291ce,” in
Military Architecture in Greater Syria
, ed. H. Kennedy (Leiden and Boston, 2006), 269–80.
Streck, M., “Biredjik,”
EI
2
1 (1960): 1233–4.
Świętosławski, W.,
Arms and Armour of the Nomads of the Great Steppe in the Times of the Mongol Expansion 12th–14th centuries
(Łodź, 1999).
Tabba, Y.,
Constructions of Power and Piety in Medieval Aleppo
(Pennsylvania State Univesity, 1977).
Tamari, S., “Two further inscriptions from ,” in
,” in
Studies in Memory of Gaston Wiet
, ed. M. Rosen-Ayalon (Jerusalem, 1977), 261–5.
——“Darb al-Hajj in Sinai: an historical-archaeological study,”
Accademia Nazionale dei Lincei Memorie
25 (1982): 431–525.
——“Darb al-Hajj, the Qal’a of Nakhl,” 23 (1983): 141–67. [Hebrew]
23 (1983): 141–67. [Hebrew]
Thorau, .,
The Lion of Egypt,
trans. P. M. Holt (New York, 1987).
Tonghini, C., Jabar Pottery: A Study of a Syrian Fortified Site of the Late 11th–14th Centuries
Jabar Pottery: A Study of a Syrian Fortified Site of the Late 11th–14th Centuries
(Oxford, 1998).
Tonghini, C., Donato, E., Montevecchi, N. and Nucciotti, M., “The evolution of masonry technique in Islamic military architecture: the evidence from Shayzar,”
Levant
35 (2003): 179–212.
Toy, S.,
A History of Fortifications, from 3000 B.C. to A.D. 1700
. 2nd ed. (London,1966).
Tracy, J. D. “To wall or not to wall: evidence from medieval Germany,” in
City Walls; the urban enceinte in global perspective
, ed. J. D. Tracy (Cambridge, 2000), 71–88.
Twain, M.,
The Innocents Abroad
(New York, 1962).
Tyerman, C. J., “Marino Sanudo Torsello and the lost Crusade: lobbying in the fourteenth century,”
Transactions of the Royal Historical Society
32 (1982): 57–73.
Verbruggen, J. F.,
The Art of Warfare in Western Europe during the Middle Ages
(Woodbridge, 1997).
Walker, B. J., “Militarization to normadization: the middle and late Islamic periods,”
NEA
62/4 (1999): 202–32.
——“Mamluk investment in Southern Bilād al-Shām in the eighth/fourteenth century: the case of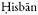 ,”
,”
JNES
62 (2003): 241–61.
Walker, B. J. and LaBianca, Ø. S., “The Islamic Qusūr of Tall Hisbān: preliminary report on the 1998 and 2001 seasons,”
ADAJ
47 (2003): 443–71.