Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine (61 page)
Read Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine Online
Authors: Marc Sabatine
Tags: #Medical, #Internal Medicine

BOOK: Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine
10.86Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
• Secondary causes: treat underlying disease • Watch for malnutrition (protein loss), thrombosis (in ~25%, esp. renal vein, b/c loss of ATIII & other endogenous anticoags), infxn (esp. encaps. organisms b/c loss of Ig)
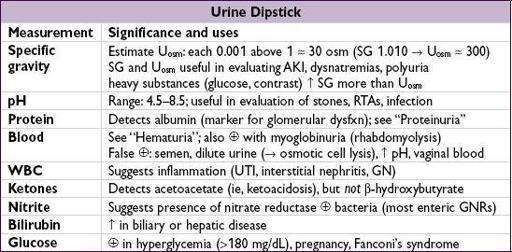
URINALYSIS
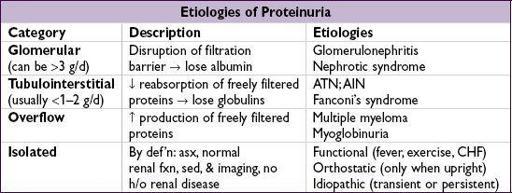
PROTEINURIA
•
Urine dipstick
1+30 mg/dL, 2+
100 mg/dL, 3+
300 mg/dL, 4+ >2 g/dL; interpretation depends on SG; eg, 3+ in very concentrated urine might not indicate heavy proteinuria
Insensitive for microalbuminuria and myeloma light chains
•
Spot urine
: protein (mg/dL)/creatinine (mg/dL)g/d of proteinuria (
NEJM
1983;309:1543) unlike urine dipstick, will accurately measure myeloma light chains reliable surrogate for 24-hr urine, esp. 1st morning void (
JASN
2009;20:436); inaccurate if AKI depends on Cr production, ∴ underestimates if muscular, overestimates if cachectic
•
Microalbuminuria
(30–300 mg/24h
or
mg/L
or
mg/mg of Cr): early sign of glomerular vascular disease; marker for ↑ risk of CV adverse outcomes (
JAMA
2001;286:421)
• Orthostatic proteinuria: typically in adolescents; ~90% of youngwith isolated proteinuria have orthostatic proteinuria; typically resolves spontaneously
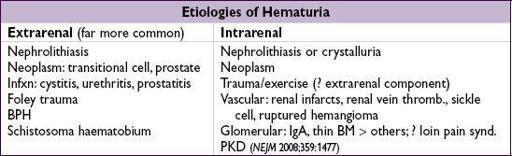
HEMATURIA
• Wide, overlapping ages for various etiologies, but general guide for common causes:
<20 y: GN, UTI, congenital; 20–60 y: UTI, nephrolithiasis, cancer
>60 y: prostatitis, cancer, UTI; >60 y
: UTI, cancer
Workup
(
J Urol
2012;188(6 suppl):2473)
•
Urine dipstick
: if ≥3 RBCs;
if ≥3 RBCs; dipstick and
dipstick and sediment → myo-or hemoglobinuria •
sediment → myo-or hemoglobinuria •
Urine sediment
: dysmorphic RBCs or RBC casts → GN → consider renal bx • If no evidence of glomerulonephritis:
Other books
The Big Black Mark by A. Bertram Chandler
The Silent Man by Alex Berenson
The Fall by Toro, Guillermo Del, Hogan, Chuck
Fake House by Linh Dinh
A Bleacke Wind (Bleacke Shifters Book 3) by Lesli Richardson
The Wedding Party by Robyn Carr
Demons Forever (Peachville High Demons #6) by Cannon, Sarra
Life Without Parole: A Kate Conway Mystery by Clare O'Donohue
One Wish In Manhattan (A Christmas Story) by Mandy Baggot