Financial Markets Operations Management (23 page)
Read Financial Markets Operations Management Online
Authors: Keith Dickinson

It is usually the case that if an investor (or its agent) wishes to invest in foreign securities, it is not possible to directly access the relevant CSD. There are two options available to the investor/agent:
- Use a custodian bank that has access to the foreign CSD (see
Figure 6.3
).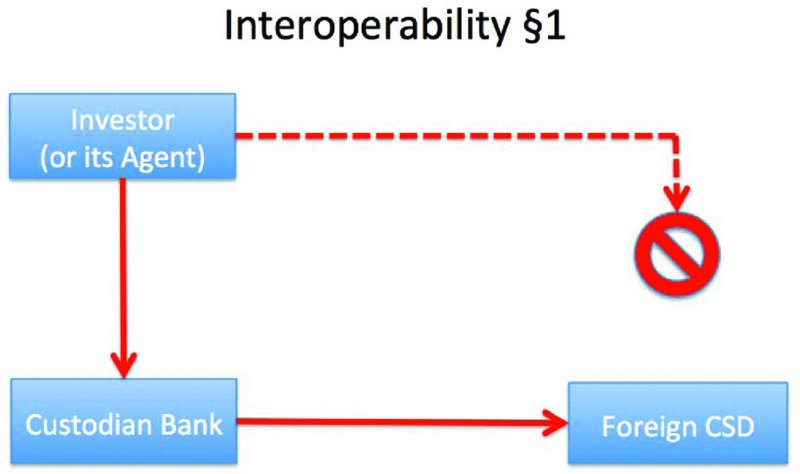
FIGURE 6.3
Custodian bank's access to foreign CSD - Use the local CSD's links with the foreign CSD (see
Figure 6.4
).
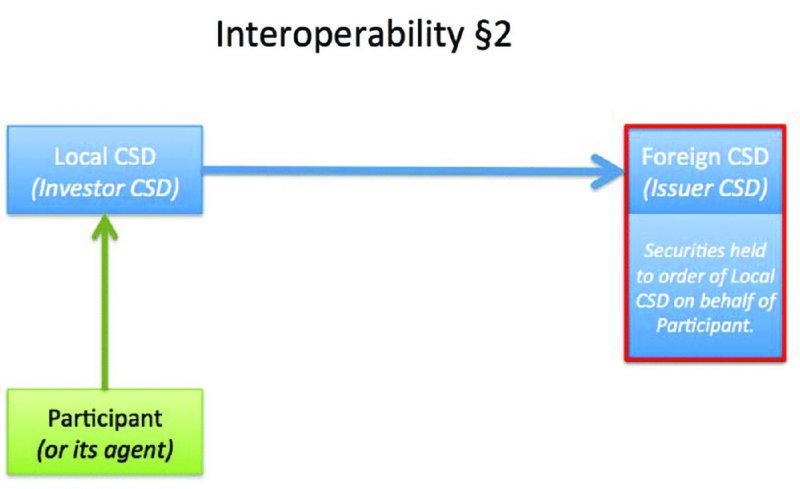
FIGURE 6.4
Local CSD's access to foreign CSD
We will look at Option 1 in Chapter 10: Custody and the Custodians. With Option 2, the link between the local CSD and the foreign CSD enables securities held in the latter to become available in the records of the former.
The local CSD (also referred to as the investor CSD) becomes a customer or participant of the foreign CSD (the issuer CSD). This would be regarded as a unilateral link. If there was a reciprocal arrangement (i.e. the issuer CSD became an investor CSD for its local investors with the original investor CSD becoming an issuer CSD), this would be a bilateral link (see
Figure 6.5
). In either event, both bilateral and unilateral links are regarded as
direct links
.
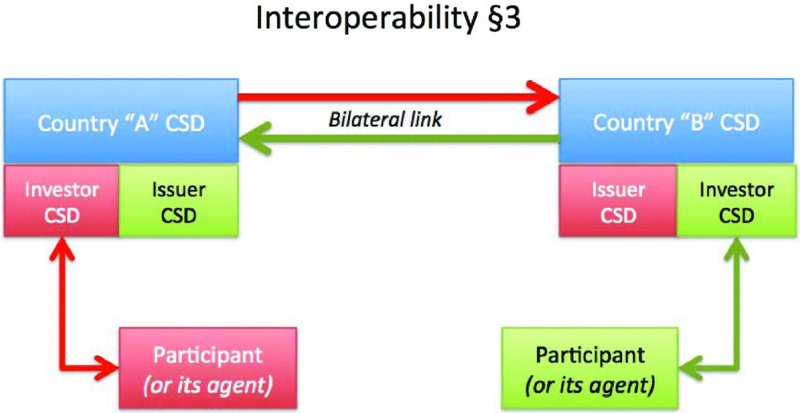
FIGURE 6.5
Direct links
Table 6.7
shows some examples of direct links.
TABLE 6.7
Direct links
| Type of Link | CSDs | Countries |
| Bilateral |
| Malta/Germany |
| Bilateral |
| Italy/Spain |
| Bilateral |
| Luxembourg/Luxembourg |
| Unilateral |
| Italy/Spain |
| Unilateral |
| Greece/Germany |
| Unilateral |
| Luxembourg/Slovakia |
Source:
European Central Bank (online) “Eligible Links as at 20 Dec 2013”. Available from
www.ecb.europa.eu/paym/coll/coll/ssslinks/html/index.en.html
. [Accessed Monday, 10 February 2014]
There is a fourth variation, known as
relayed links
, whereby two CSDs are linked using a third as an intermediary CSD (see
Figure 6.6
).
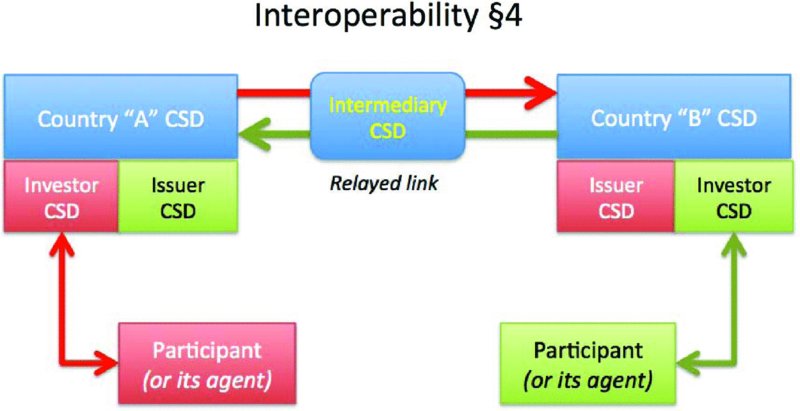
FIGURE 6.6
Relayed links
Examples of relayed links include the following:
6
6
- Germany: Clearstream Banking AG via Clearstream Banking Luxembourg to Monte Titoli (Italy);
- France: Euroclear France via Euroclear Bank (Belgium) to Clearstream Banking AG (Germany);
- Luxembourg: LuxCSD via Clearstream Banking Luxembourg to KDD (Slovenia).
These links would allow securities to be delivered on a free of payment (FoP) and/or a delivery/receive against payment (DVP/RVP) basis.
Euroclear Bank and Clearstream Banking Luxembourg, the two international CSDs, are regarded as fully interoperable with their use of the bridge (see the next section).
In Section 6.2 of this chapter, we gave a brief overview of the events that led to the creation of the two international central securities depositories (ICSDs). The formation of Euroclear and Cedel occurred against the background of the issuance of physical Eurobond certificates and the problems associated with the delivery of the certificates to the various European centres where the underwriters, dealers and investors were located.
Morgan Guaranty's Brussels office was used to host the issuers' closing ceremonies that included the handing over of the new bonds to the lead underwriter. It was decided to launch a system whereby the physical certificates were replaced by a book-entry system and where receipts and deliveries against payment could occur once participants had opened securities accounts and cash accounts with the system. That system became Euroclear and it was founded in December 1968.
Whilst bond closings took place in Brussels, most Eurobonds were listed in Luxembourg. Luxembourg was also experiencing operational logjams in New York. Luxembourg-based banks, both local and foreign, decided to investigate the establishment of a rival system to Euroclear. By September 1970, the Centrale de Livraison de Valeurs Mobilières, better known as Cedel, was launched by 71 banks from 11 countries with the motto: “By the market, for the market”.
So we can see that in a very short period of time, one particular product type with no national domicile, the Eurobond, could be held and processed out of two systems, both based in continental Europe. The history of these two organisations makes for interesting reading and their fierce competitiveness over the years has been good for the industry across a wide range of areas, including:
- Communication;
- New products;
- Services (both core and value-added).
The ICSDs are similar to the basic concept of a CSD but differ in one important respect: Euroclear and Clearstream are banks and this enables them to offer credit and certain other banking activities related to security settlement.
It can be argued that the ICSDs are as much a part of the post-trade market infrastructure as the CSDs except that the ICSDs are commercial in nature; in other words, they not only look after their customers but also their shareholders.
Whilst both ICSDs are similar to a clearing house and CSD combination, it should be noted that the ICSDs do not act as central counterparties. Their services cover the entire spectrum from new issuance to redemption.
CBL settles a wide range of securities including:
- International debt securities, including global bonds and Eurobonds (straight, floating-rate, convertible etc.);
- Foreign bonds;
- Money market instruments, including short- and medium-term notes, commercial paper and certificates of deposit;
- Domestic bonds (government and corporate);
- Equities;
- Depository receipts;
- Investment funds;
- Warrants;
- Asset-backed securities and other collateralised debt securities.
CBL offers a full range of services from advice to primary distribution using its Global Issuer Hub:
- Advisory services:
Supporting lead managers, lawyers, issuers and their agents; - Securities admission:
Eligibility checks and compliance checks prior to admission to the Global Issuer Hub; - Code allocation:
CBL is the numbering agent for international ISIN codes; - Electronic document transfer:
This enables the securities to be delivered electronically, rather than physically; - Primary market distribution:
Supports issuers and their agents in distributing the securities to investors.
CBL has three types of settlement:
- Internal settlement for transactions between two CBL participants.
- External settlement for transactions with non-ICSD participants.
- Bridge settlement for transactions between CBL and Euroclear participants.
Transactions can be settled on either a DVP/RVP or free of payment (FoP) basis.
CBL processes income and corporate actions activities together with reports that include income pre-advices, corporate action notifications and market claims.
CBL provides a full range of securities financing services through its Global Liquidity Hub, including:
- Triparty collateral management and general collateral (GC) pooling;
- Automated securities lending and borrowing for fails management and strategic lending.
CBL's Vestima Funds Hub provides the link between investor, fund distributor, transfer agent and trading platform. The Vestima Funds Hub enables:
- Order routing to funds (or their agents) or to trading platforms;
- Post-trade settlement by DVP in commercial bank money;
- Collateral using investment funds as an eligible asset class in the triparty repo service;
- Value-added services including funds reference data and real-time reporting.
We have seen in the previous section that there are direct links between the ICSDs and a selection of local CSDs. These links can either be unilateral or bilateral in nature.
Participants can input instructions, access information, manage corporate action activities, send queries and handle exceptions using one or more connectivity products offered under the CreationConnect service. The three products are:
- CreationOnline:
Via the Internet or a virtual private network (VPN); - CreationDirect:
By file transfer using the Internet, the Clearstream VPN, Lima or SWIFTNet FileAct; - Creation via the SWIFT network:
Link through SWIFTNet FIN.
In September 2013, CBL launched ClearstreamXact, an Internet-based system that initially offers participants access to CBL's collateral management service. (Settlement and asset management are planned additional services.)
EB processes a wide range of securities including:
- International bonds, including foreign bonds, global bonds and Eurobonds;
- Domestic debt;
- Convertible bonds;
- Warrants;
- Equities;
- Depository receipts;
- Investment funds.
EB helps issuers, lead managers and issuing agents by:
- Helping to identify new issue structures;
- Allocating identification codes to new securities (EB is a numbering agency);
- Providing DVP issuance of the securities;
- Providing relevant administrative services.
EB, as with CBL above, has three types of settlement:
- Internal settlement for transactions between two Euroclear participants.
- External settlement for transactions with non-ICSD participants.
- Bridge settlement for transactions between EB and CBL participants.
Transactions can be settled on either a DVP/RVP or free of payment (FoP) basis.
These services include:
- Corporate action notifications;
- Real-time processing and reporting;
- Income and redemption processing;
- Withholding tax assistance;
- Proxy voting market claims management.
This includes collateral management and securities lending and borrowing.
Money transfer facilities include:
- Book transfers: Internal payments between participants within the EB system;
- Wire transfers: External payments made by participants outside the EB system;
- Pre-advices: Incoming payments for EB participants from outside the EB system;
- Foreign exchange services.
EB provides credit facilities to enable participants to manage their operations, especially settlements, borrowing and money transfer. Credit facilities are provided on a secured basis.
EB's investment fund platform is FundSettlement International, which provides a single access point for fund management companies, fund distributors and transfer agents. Users have access to:
- Order validation;
- Funds settlement;
- Corporate actions processing;
- Real-time reporting;
- Client support.
We have seen in the previous section that there are direct links between the ICSDs and a selection of local CSDs. These links can either be unilateral or bilateral in nature.
Participants can access Euroclear through the following Internet Protocol-based networks:
- Radianz
- Infonet
- SWIFTNet
- The Internet.
Applications are either screen-based or computer-to-computer â see
Table 6.8
.
TABLE 6.8
Screen-based or computer-to-computer connectivity
| Screen-Based | Computer-to-Computer |
| EUCLID PC â settlement instruction/validation plus reporting | EUCLID server |
| FundSettle â access to FundSettle International service | EUCLID file transfer |
| Triweb and Biweb â collateral management reporting | FundSettle file transfer |
| SWIFT |
Instructions can also be submitted by tested telex, post and, exceptionally, fax (with telephone call-back).