Financial Markets Operations Management (24 page)
Read Financial Markets Operations Management Online
Authors: Keith Dickinson

We have now examined the three main elements to the infrastructure of the industry:
- Stock exchanges;
- Clearing systems; and
- Central securities depositories.
We can add two more elements â the international CSDs and cash payment. The two ICSDs are banks and payment occurs through “commercial bank money”. The national CSDs are linked to their national central banks and payment here is said to be in “central bank money”.
Let us compare the linkages from three points of view:
- The USA.
- The European region.
- The rest of the world, including the Asia-Pacific, Africa/Middle East and the Americas regions.
This comparison will illustrate that the USA is centralised, Europe is fragmented and Asia-Pacific is domestically focused. We will see in the next section that several CSD associations have been formed in order to introduce regional cooperation if not actual consolidation.
The European Central Bank published a brochure in November 2009
7
7
which summarised the linkages that existed in Europe and the USA. Reading this will give you an idea of just how complex the situation is in Europe.
In the USA, corporate bonds and equities are cleared through the Depository Trust & Clearing Corporation (DTCC) and government securities, federal agencies and government-sponsored entities are processed through the Federal Reserve System (the “Fed”).
In
Figure 6.7
, you can see just how centralised the USA landscape is.
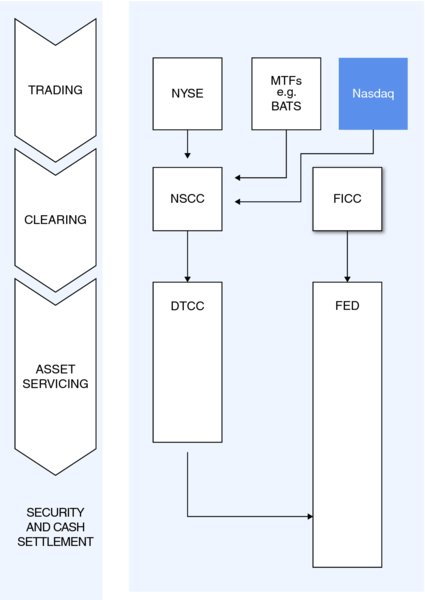
FIGURE 6.7
Linkages in the USA
Source:
ECB 2009 “Settling without Borders”.
By comparison, Europe is very much more fragmented and complex (see
Figure 6.8
).
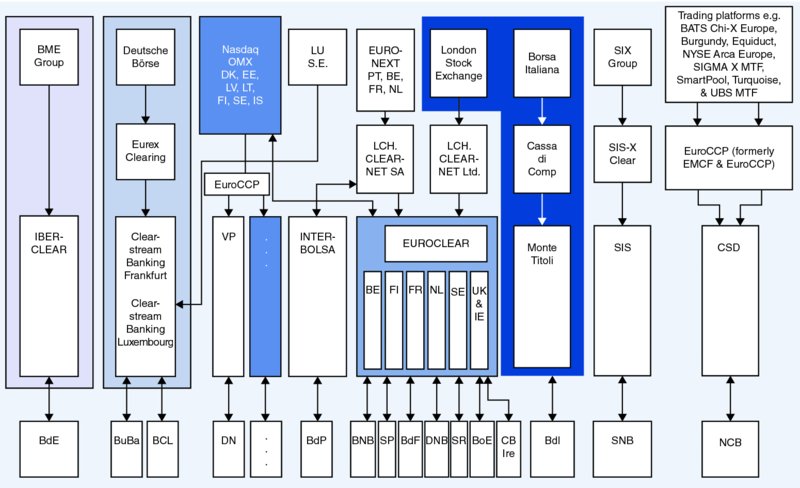
FIGURE 6.8
Linkages in Europe
Source:
ECB 2009 “Settling without Borders” plus updates by author.
As we can see from
Figure 6.8
, the situation in Europe is that of a highly fragmented clearing, settlement, custody and payment environment.
- The shaded boxes indicate groups of companies resulting from mergers and acquisitions, including:
- In Spain, Germany, countries in the Nasdaq OMX group and Italy, there is a vertical silo approach (
vertical integration
) whereby the stock exchange, clearing system and CSD are part of the same national group. - The UK and Italian stock exchanges are also part of the same group, albeit with different clearing systems and CSDs.
- The Euroclear group includes the national CSDs of six countries. This is known as
horizontal integration
. - EuroCCP sends transactions to the appropriate local CSD for settlement.
- In Spain, Germany, countries in the Nasdaq OMX group and Italy, there is a vertical silo approach (
Outside of Europe, the landscape is closer to the USA “model”, with each country supporting an exchange, clearing system, CSD and payment system.
There are five CSD associations based regionally:
- Americas' Central Securities Depositories Association (ACSDA).
- Asia-Pacific CSD Group (ACG).
- Association of Eurasian Central Securities Depositories (AECSD).
- European Central Securities Depositories Association (ECSDA).
- Africa and Middle East Depositories Association (AMEDA).
In 2011 the five associations formed the World Forum of CSDs to enhance communication between the associations.
This is a non-profit organization comprised of Central Securities Depositories and Clearing Houses of the Americas, headquartered in Lima, Peru. Its by-laws were established at the first General Assembly held in the city of Lima, Peru on August 10, 1999.
ACSDA's main purpose is to be a forum for the exchange of information and experiences among its members in a spirit of mutual cooperation and to promote best practice recommendations in services such as securities depository, clearance, settlement, and risk management. ACSDA's goal is also to support local markets in their efforts to adopt securities market regulations, while considering their specific circumstances and to serve as a channel for dialogue with other organizations worldwide.
Source:
www.acsda.org
There are 18 member CSDs including Strate (South Africa)!
The Asia-Pacific Central Securities Depository Group (ACG) was formed in November 1997 as an informal international organization with the objective to facilitate the exchange of information and to promote mutual assistance among member securities depositories and clearing organizations in the Asia-Pacific region.
Source:
www.acgcsd.org/acg_01.aspx
There are 32 member CSDs from 22 countries.
The Association, founded in 2004 with the aim being: “â¦Â the formation of a common âdepository environment', including harmonization of the regulatory and legal framework, development of an optimal recordkeeping system for the securities market and the organization of effective interaction among the member organizations to ensure efficient cross-border securities transfers. Moreover, the question of standardization of depository technologies, development of the electronic document exchange and adoption of international messaging standards for depository transactions are high on the agenda.”
Source:
www.acde.ru/about_eng.php
The founding membership consisted of 11 entities from 10 countries.
ECSDA's objective is to offer solutions and provide advice at international level on technical, economic, financial and regulatory matters to reduce risk and increase efficiency in custody, pre-settlement and settlement arrangements for securities and related payments across Europe for the benefit of issuers, investors and market participants.
Source:
www.ecsda.eu
There are 41 member national and international CSDs from 37 countries. Russia and Ukraine are also represented on the AECSD.
Established in 2005, AMEDA's main purpose is to be: “â¦Â a forum for the exchange of information and experiences among its members in a spirit of mutual cooperation and to promote best practice recommendations in services such as securities depository, clearance, settlement, and risk management.
Its goal is also to support local markets in their efforts to adopt securities market regulations, while considering their specific circumstances and to serve as a dialogue channel with other organizations worldwide.”
There are 25 member CSDs from 24 countries.
The safekeeping of securities has evolved from being fragmented to being centralised. Fragmented safekeeping includes situations where securities are held in one of the following ways:
- By the investor;
- By the investor's agent (e.g. bank, legal representative);
- By the investor's bank/custodian.
Centralised safekeeping is where the issuer deposits the entire issue with a central securities depository (CSD). The securities are either in physical form or book-entry form. Securities that were originally issued in physical form can be processed through book entries across participants' securities accounts.
CSDs provide services that range from basic safekeeping and settlement to asset optimisation and securities financing. Whilst CSDs are local, i.e. they handle securities issued in their local markets, they can link to other CSDs.
The two international CSDs, Euroclear Bank and Clearstream Banking Luxembourg, were originally established to handle Eurobonds â securities that have no domicile. The services offered range from new issuance to settlement and safekeeping, money transfer, securities optimisation, income collection and bond redemptions, i.e. from the start of a bond to the finish. The ICSDs are now able to handle a wide range of asset types due to their links with several local CSDs.
Post-trade processing is generally centralised in most regions (e.g. USA) except for Europe where it is very fragmented.
There are five regional CSD associations covering the Americas, Asia-Pacific, Africa and the Middle East, Eurasia and Europe. These associations look after the interests of their CSD members.