Muslim Fortresses in the Levant: Between Crusaders and Mongols (143 page)
Read Muslim Fortresses in the Levant: Between Crusaders and Mongols Online
Authors: Kate Raphael
Tags: #Arts & Photography, #Architecture, #Buildings, #History, #Middle East, #Egypt, #Politics & Social Sciences, #Social Sciences, #Human Geography, #Building Types & Styles, #World, #Medieval, #Humanities

67 Ibn Shaddād,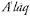 , vol. 1, pt. 1, 145.
, vol. 1, pt. 1, 145.
68 Amitai, “ ,” 114.
,” 114.
69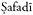 ,
,
Wafayāt
, vol. 10, 366; Irwin,
Middle East
, 62; Amitai-Preiss,
Mongols
, 179–80.
70 Mayer, L. A.,
Islamic Architects and Their Works
(Geneve, 1956), 18–26.
71 Behrens-Abouseif, D., “Muhandis, Shād,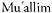 – note on the building craft in the Mamluk period,”
– note on the building craft in the Mamluk period,”
DI
72 (1995), 295; Amitai, “ ,” 116.
,” 116.
72 Rabbat, N., “Architects and artists in Mamluk society: the perspective of the sources,”
Journal of Architectural Education
52 (1998): 32.
73 Mayer,
Islamic Architects
, 27.
74 Behrens-Abouseif, D.,
Islamic Architecture in Cairo: An Introduction
(Leiden and New York, 1989), 18.
75 Irwin,
Middle East
, 55; Amitai, “ ,” 109–23. See especially 114–15.
,” 109–23. See especially 114–15.
76 Humphreys, R. S., “The emergence of the Mamluk army (conclusion),”
SI
46 (1977): 175–7.
77 Ibn Shaddād,
Ta’rīkh
, 354.
78 Apart from the urban fortifications, round towers can be seen at Arsuf, Crac des Chevaliers, Margat.
79 Keen, M., “The changing scene: guns, gunpowder and permanent armies,” in
Medieval Warfare
, ed. M. Keen (Oxford, 1999), 273–91.
80 Hartal, M.,
The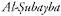 (Nimrod) Fortress, Towers 11 and
(Nimrod) Fortress, Towers 11 and
(Jerusalem, 2001), 69.
81 Ibid., 23.
82 Ibn Shaddād, , vol. 1, pt. 1, 82.
, vol. 1, pt. 1, 82.
83 Hartal, , 36–7.
, 36–7.
84 Excavations at the citadel: Damati, E., “ Safed,”
ESI
4 (1985): 98; ibid., “Safed,”,
ESI
5 (1986): 93–4; ibid., “Safed Citadel,”
ESI
, 1988/89, vols 7–8, 159–60; ibid., “Safed Citadel,”
ESI
9 (1989/90): 13. More recently excavations were conducted by Barabé, H. and Damati, E., “La forteresse médievale de Safed: données récentes de l’archéologie’,”
Crusades
3 (2004): 171–3. I would like to thank Haim Barabé for his help and explanations concerning the plan of the fortress and some of the debates concerning the dating of the gate structure he excavated.
85 Ibn al-Furāt,
Ta’rīkh
(Lyons), vol. 2, 88; Amitai-Preiss, R., “ ,”
,”
EI
2
8:757.
86 A full translation is given in Kennedy,
Castles
, 190–8. The most compehensive examination of this source is by R. B. C. Huygens,
De constructione castri Saphet: construction et functions d’un chateau fort franc en Terre Sainte
(Amsterdam, Oxford and New York, 1981); Pringle, D., “Reconstructing the Castle of Safad,”
PEQ
117 (1985): 139–49.
87 Dunlop, D. M., “Dimashqī,”
EI
2
2:291.
88 When he returned he was employed as a clerk in the administration of Safad. Rosenthal, F., “ ,”
,”
EI
2
8:759.